Translate this page into:
Research on the environmental science and sustainable sport development the perspective of geological ecology
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
This article was originally published by Elsevier and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Peer review under responsibility of King Saud University.
Abstract
The development model of traditional sports tourism basically starts from the perspective of operation, development and management, but ignores the overall consideration of economic and social benefits and ecological environmental protection. In order to avoid or reduce the negative impact of sports tourism on the environment, the development of ecological sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology is the top priority for the healthy and sustainable development of sports tourism. On the basis of summarizing and analyzing previous research results, this paper introduced the methods and principles of carrying capacity of geological ecology and environmental system of sports tourism, conducted the model construction of environmental science for sports tourism, analyzed the optimization strategy of environmental science for sports tourism, constructed the environmental science of sports tourism based on geological ecology, performed the resource integration of sustainable development for sports tourism, proposed the functional integration of sustainable development for sports tourism, explored the sustainable development of sports tourism based on geological ecology, and finally discussed the relationship between sports tourism and geological ecological capacity and the achieving approaches for sustainable development of sports tourism. The study results show that for environmental science, its overall benefits range from 43% to 72% with an average of 58%; for sustainable development, that range from 55% to 79% with an average of 68%. For environmental science, the resource integration of sports facilities decrease from 95% to 66% when geological ecological capacity range from 40% to 90%; for sustainable development, that of sports facilities decrease from 91% to 59% when geological ecological capacity range from 40% to 90%. The environmental science and sustainable development of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology can ecologically and organically combine sports activities and tourism activities in accordance with scientific and reasonable concepts, develop various sports that can satisfy tourist demands, and can achieve ecological, economic and social benefits of ecological sports tourism. The study results of this paper provide a reference for further researches on the environmental science and sustainable development of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology.
Keywords
Sports tourism
Environmental science
Sustainable development
Geological ecology
1 Introduction
Sports tourism is based on sports resources and certain sports facilities and is in the form of tourism products, which can provide tourists with a business project group integrating various activities such as fitness, entertainment, leisure, and communication during travel and sightseeing. Sports tourism has become a worldwide trend, but at the same time as it develops, the damage to the environment by tourism is becoming more and more serious (González-García et al., 2022). For the development of tourism, the huge environmental problem is a severe challenge to the in-depth and lasting development of the tourism industry and the severe environmental crisis has made the capacity of the tourism environment gradually decrease (Johann et al., 2022). Therefore, sports tourism must follow the laws of ecology in planning, development, utilization, and management, with the concept of sustainable development as the guiding ideology, study the carrying capacity of sports tourism, control the ecological capacity, ensure the beauty of the ecological environment, and maintain the resources of sports tourism. If tourism does not adopt a sustainable development model, the development of the entire tourism industry will be unsustainable (Wang and Zhang, 2019). When there is a conflict between economic goals and geological and ecological goals, tourists can abandon their own economic interests without hesitation and protect the geological ecology and ecology. Looking at the overall strategic layout and development planning of the sports tourism industry from the perspective and perspective of the upstream and downstream industrial chain, the environmental science of sports tourism needs to explore the combination of sports and tourism in the new era and form innovation to create a sustainable sports tourism situation (Scheyvens, 2018).
Sports tourism organically combines physical activity with traditional tourism elements, which not only satisfies people’s desires for sightseeing, shopping, and leisure, but also maximizes participation, meets modern people’s needs for fitness and entertainment, and gives people greater excitement (Marrosu and Balvis, 2020). The sports tourism environmental system formed by its development is a composite system that is composed of social, natural, economic and other elements and is conducive to sustainable development, whether it is qualitative elaboration or quantitative analysis, many factors are involved. In combination, develop ecological sports tourism that not only meets the various sports needs of tourists, but also realizes ecological, economic and social benefits (Mostafanezhad and Norum, 2019). The traditional sports tourism development model basically starts from the perspective of business development and management, but ignores the combination of human leisure experience and inner needs with ecological protection, which is the foothold of this research (McCullough et al., 2020). Sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology should be vigorously developed in areas with suitable altitude, lush vegetation, adequate water sources, suitable geomorphic features, convenient transportation, and abundant resources for surrounding tourism and skiing populations, and encourage the construction of large-scale, high-level and international modern bases to ensure the rational use of the environment and resources (Kırlı and Fahrioğlu, 2019).
On the basis of summarizing and analyzing previous research results, this paper expounded the research status and significance of the environmental science and sustainable development of sports tourism, elaborated the development background, current status and future challenges of geological ecology, introduced the methods and principles of carrying capacity of geological ecology and environmental system of sports tourism, conducted the model construction of environmental science for sports tourism, analyzed the optimization strategy of environmental science for sports tourism, constructed the environmental science of sports tourism based on geological ecology, performed the resource integration of sustainable development for sports tourism, proposed the functional integration of sustainable development for sports tourism, explored the sustainable development of sports tourism based on geological ecology, and finally discussed the relationship between sports tourism and geological ecological capacity and the achieving ways for sustainable development of sports tourism. The detailed chapter arrangement is as follows: Section 2 introduces the methods and principles of carrying capacity of geological ecology and environmental system of sports tourism; Section 3 constructs the environmental science of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology; Section 4 explores the sustainable development of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology; Section 5 discusses the relationship between sports tourism and geological ecological capacity and the approaches for sustainable development of sports tourism; Section 6 is conclusion.
2 Methods and principles
2.1 Carrying capacity of ecological ecology
The reason for the generalization of the concept of sports tourism is, on the one hand, the complexity of the new form of sports tourism; on the other hand, researchers have not answered what is sports tourism from the perspective of sports tourism participants, and what sports tourism should conform to. Such rules lack an overall study from the perspective of the main stakeholders of sports tourism. Environmental science must first fully realize that sports tourism is not only the tourism development, protection and sustainable development of the natural ecological environment, but also the tourism development, resource protection and sustainable development of the natural ecology and cultural ecology, and understand here (Brankov et al., 2017). They develop strict sports tourism codes of conduct and tourism business codes of conduct on the basis of the above-mentioned policies, advocate low-carbon tourism forms, and increase natural environment and humanistic education and publicity for local residents, tourists and tour operators. Tourism operators believe that sports tourism is the development of natural resources and provide tourists with travel experience products that return to nature and enjoy nature. Tourists’ understanding of sports tourism is in a dim state. Under the guidance of operators, they believe that the products provided by sports tourism operators are so-called sports tourism products, and sports tourism is a natural tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology.
Sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology requires orderly planning of sports tourism functional areas, rational development of sports tourism projects according to the characteristics of functional areas and sports tourism resources, not blindly rushing, not in fragile ecological resources or key protected areas development. The environmental science of sports tourism should be developed in an orderly manner in accordance with the evolution of tourism resources, and the value of sports tourism resources should be calculated to prevent the obvious growth of sports tourism economy from being emphasized, and the hidden losses caused by the destruction of tourism resources should be ignored. Only by emphasizing the value of tourism resources, the sports tourism can the sustainable development of sports tourism ecology be realized. Behind the benefits of these sports tourism industries, all kinds of abandoned mountaineering equipment and domestic garbage have caused huge pollution to the fragile ecological environment. The increasing demand for sports tourism has exceeded the physical, biological, and psychological capacity of the ecological environment, affecting the sustainable development of sports tourism. In addition, sports tourism management personnel ignore ecological management, sports tourism personnel have poor environmental awareness, and the tourism tools used are polluting, and their own carrying and excreted garbage cannot be environmentally treated, which brings pollution to sports tourism resources.
2.2 Environmental system of sports tourism
The tourism environment index refers to the ratio of the environmental carrying capacity of a tourist destination to the carrying capacity of the tourist environment. The carrying capacity of tourism environment is a comprehensive concept, which is composed of the carrying capacity components of different tourism environment elements, and it is composed of the carrying capacity components of the environmental elements of different tourist destinations. The environmental carrying capacity of ecotourism focuses on the environmental carrying capacity of ecotourism. The sustainability of economic development mainly means that the economic benefits obtained by the tourism reception area through the development of tourism must be able to compensate for any direct costs paid for receiving tourists’ visits, as well as to prevent and eliminate various negative impacts caused by tourism. The social costs of taking necessary measures and actions to deal with the problems, and should also enable the residents of the tourism reception area to receive appropriate economic compensation for the various inconveniences suffered in the development of tourism (Priyadarshini and Abhilash, 2020). The social factors of sports tourism play a role in guaranteeing the sustainable development of sports tourism. A strong sports culture atmosphere, a stable and harmonious social environment, and a good social image will all attract the attention of investors from outside the region and inject new vitality into the local economic development (Fig. 1) The local sports tourism resources are properly protected, and the talents of sports tourism have the capacity for sustainable development; a good sports tourism environment will help improve the local social image and economic income.
Environmental system of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology.
Sports tourism has become a worldwide trend, but at the same time of its development, the damage to the environment by tourism is becoming more and more serious. As the concept of organic integration of tourism development and geological ecological protection is deeply rooted in the hearts of the people, the scope and space of sports tourism continue to expand. Sports tourism will be accepted by the mainstream market and become a popular new form of modern mass tourism, whether it is the number of tourists or tourism. Income will occupy an increasingly important position in the tourism system and sports tourism emphasizes that tourism objects should not be harmed. As a new type of tourism activity, sports tourism, compared with sports tourism, its biggest feature is to emphasize the protection of tourism objects. In the traditional sports tourism management, the idea of emphasizing economy and over-environmental protection makes it pursue short-term economic benefits. Sports tourism follows ecological laws in planning, development, utilization, and management, and takes the theory of sustainable development as the guiding ideology. Sports tourism planners study the carrying capacity of sports tourism, control the ecological capacity, ensure the beauty of the ecological environment, and maintain the continuous use of sports tourism resources. Environmental science is mainly embodied in promoting the virtuous cycle of the natural ecological environment, promoting the protection of organisms, promoting the protection of water bodies and the treatment of water pollution, and has a good protective effect on the atmospheric environment and geological landforms.
3 Environmental science of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology
3.1 Model construction of environmental science
From the perspective of time distribution, tourism activities are seasonal. As the geological ecological environmental factors, socio-economic factors, local residents’ psychological factors and management suitability in tourist areas change regularly over time, the resource space capacity and economic capacity determined by these influencing factors, socio-psychological capacity, and management service capacity also change over time. In this way, the sum of the above-mentioned capacity components is finally determined, that is, the environmental capacity of sports tourism has the characteristics of time distribution. From the perspective of spatial distribution, the geological ecological environment, which is the basis of tourism environmental capacity, has spatial differences in its ecological resilience, sensitivity and other characteristics, and there are also regional differences in socio-economic environment and social psychology. Therefore, sports tourism environmental capacity has spatial differences and tourism with different characteristics is a comprehensive industry (Safarabadi, 2016). In order to avoid or reduce the current negative impact of sports tourism on the environment, the development of ecological sports tourism is a top priority for the healthy and sustainable development of sports tourism. Sports tourism planners study the carrying capacity of sports tourism, control the ecological capacity, ensure the beauty of the ecological environment, and maintain the continuous use of sports tourism resources. Especially when quantifying the capacity of tourism environment, it is more necessary to cross-discipline and multi-field to conduct comprehensive research. Fig. 2 shows the framework of the environmental science and sustainable development of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology.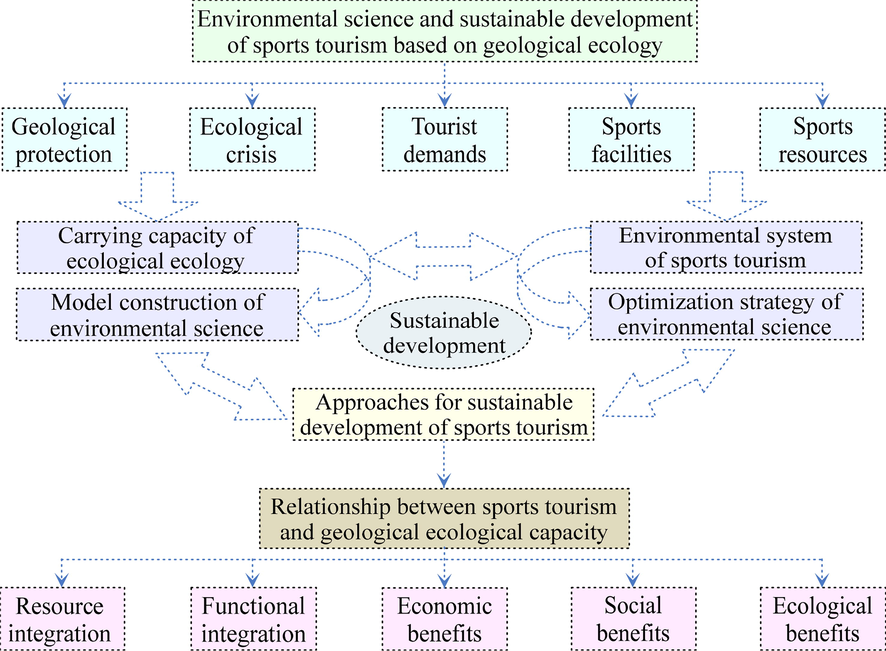
Framework of the environmental science and sustainable development of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology.
Before the development of sports tourism resources, it is necessary to fully demonstrate the possible impact of the development on the geological ecology, and strive to minimize the impact of the development on the environment. Throughout the development process, ecological inspections are carried out at all times, and the project construction process is evaluated to reduce the negative impact of the construction process on the geological ecology. The environmental science of sports tourism requires timely collection of relevant environmental data, detailed analysis of the data using the database, and finding out the resource usage and geological and ecological pollution during the construction process, paying attention to all kinds of pollution during the construction process, and controlling all kinds of pollution as reasonable as possible within range. The sustainable development of sports tourism requires strengthening the research on the environmental carrying capacity of the scenic spot, comprehensively evaluating the resources, environment, ecology, and economy of the scenic spot, and finding a threshold range suitable for the combination of economic development and ecological protection of the scenic spot. The development of sports tourism must make full use of the advantages of big data, collect, process, analyze, and in-depth data on the environmental carrying capacity of the scenic spot, and conduct empirical analysis of the data through the model, so as to provide data support for the strategic planning of the scenic spot. It will also focus on studying the time dynamic impact of the environmental carrying capacity of the scenic spot, the correlation between various elements, and the temporal and spatial coupling of the environmental carrying capacity, and promote the sustainable development of the scenic economy through the cutting-edge technology of the environment (da Silva and da Silva, 2019).
From the perspective of cost, the sports tourism industry consumes fewer resources than many other industries, and many resources can be used continuously. Therefore, the development of sports tourism itself is an integral part of the sustainable development goal system and an advantageous industry with sustainable development. Sports tourism organically combines physical exercise with traditional tourism elements. While satisfying people's desires for sightseeing, shopping, and leisure, it also satisfies modern people's needs for fitness and entertainment. However, in the current development of sports tourism, people pay more attention to the economic and social promotion of sports tourism, and often ignore the natural environmental pollution, geological and ecological damage, and the disappearance of local characteristics caused by the development of sports tourism and the over-exploitation of sports tourism resources. For this reason, the environmental science of sports tourism must conduct in-depth research on the sustainable development of the tourism industry based on the theory of sustainable development, so as to provide a basis for the sustainable development of sports tourism. The sustainable development of sports tourism is based on the appropriate development of people, the sustainable utilization of sports tourism resources and the continuous improvement of the carrying capacity of the ecological environment. The key is to coordinate the relationship between tourism development and resource environmental protection, and achieve tourism ecology.
3.2 Optimization strategy of environmental science
Sports tourism is a new form of tourism, and its development time is very short and the exact concept of it is not perfect at present. Different researchers have studied the development goals, development conditions, functions and principles of sports tourism and what tourists should bear. Obligations and activity forms have different understandings and definitions, which is what makes sports tourism different from general natural sightseeing tours. All creatures on the earth have the right to an environment free from pollution and destruction, and the right to be able to survive and develop. In the process of developing sports tourism, the right of natural objects must be fully respected (Fig. 3). Planning, development, and operation are fully reflected in the process of management and tour. This principle requires that in the development of tourism, the immediate economic benefits should be consciously combined with the long-term geological and ecological benefits, with as little input, more output, more use, reuse, and less emissions as possible. The geological ecology should be regarded as a kind of potential productivity should be protected, and the principle of geological ecological balance should be used to restrict and regulate tourism activities, that is, to arrange various tourism activities in accordance with the geological ecological point of view, and not violate the laws of geological ecology, so that tourism activities can achieve economic and geological ecological benefits and simultaneous optimization.
Optimization strategy modes of environmental science (a) and sustainable development (b) of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology.
In order to avoid or reduce the current negative impact of sports tourism on the environment, the development of ecological sports tourism is a top priority for the healthy and sustainable development of sports tourism. In combination, develop ecological sports tourism that can not only meet the various sports needs of tourists, but also realize ecological, economic and social benefits. When selecting sports venues, it is necessary to fully consider the local weather and climate, topography, vegetation and hydrology and other relevant conditions. Under the premise of natural conditions permitting, the design, site selection and construction of sports venues should take into account the maintenance of the stadium during operation. The original natural conditions should be used as much as possible to avoid large-scale changes to the local topography, vegetation, and hydrology (Cetin et al., 2018). In the process of developing the ecology of sports tourism, it is necessary to fully consider the sports characteristics of the project sports, combine the local natural environment, scientifically plan, make full use of the local natural resource advantages, and develop appropriate sports according to local conditions. For tourism projects, avoiding increasing investment in the development of sports projects under the premise that natural condition cannot meet or adapt to the requirements of sports projects.
The rational development and utilization of resources is conducive to the healthy and sustainable development of the sports tourism market. Excessive development and utilization has caused serious damage and pollution to vegetation, forests, geology, and landforms. Although the government must integrate environmental protection when advocating the development of sports tourism resources, the infrastructure construction of tourism facilities, such as roads, hotels, bridges and recreational facilities will inevitably have an impact on the surface, water resources, and animals, destroying the rich and complex natural ecosystem. The development of sports tourism projects must adhere to the principle of sustainable utilization for appropriate development, and the ecological environment cannot be ignored because of market economic benefits. Excessive development will only bring temporary economic benefits and will also curb the development of sports tourism in the future (Drosos et al., 2016). Therefore, whether it is from the development of regional economy and society, or from the development of sports tourism, we must do a good job in the protection of air quality, the protection of water and soil resources, and the protection of the animal ecosystem. Reasonable development and permanent utilization of the township coordinate social benefits and economic benefits, the relationship between overall benefits and local benefits, actively improve the local ecological environment, and make effective use of sports tourism resources to play a positive role in environmental protection promotion.
4 Sustainable development of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology
4.1 Resource integration for sustainable development
Compared with mass tourism, the development of sports tourism requires strict conditions to proceed. Specifically, the development of sports tourism requires not only tourism developers who are familiar with tourism and better understanding of geological and ecological protection, but also tourism operators who are sincere in geological and ecological protection. When there is a conflict between economic goals and geological and ecological goals, tourists can abandon their own economic interests without hesitation and protect the geological ecology and ecology (Chen et al., 2019). Obviously, it is not easy to achieve this under the current large geological ecology where tourism development from the government to the enterprise generally pays attention to economic benefits. In order to ensure the normal progress of sports tourism, it is necessary to implement sports tourism management mechanisms and government governance models to regulate corporate and individual behaviors and ensure the balance of interests of all tourism stakeholders to promote the sustainable development of sports tourism areas (Fig. 4). Sports tourism is mostly carried out in areas where geological heritage landscapes and ecological geological ecosystems are relatively fragile, which also needs a group of responsible sports tourists with high quality, luxury enjoyment for the geological ecology. Therefore, sports tourists should be positioned as a group of tourists with high income, high environmental awareness, and a sense of geological and ecological responsibility, which are basically consistent with the requirements of sports tourists.
Resource integrations for substantial development of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology.
The blind construction of sports tourism venues not only destroys the local geological ecology, but also affects the cultural environment and natural landscape, destroying the local tradition, history, and ethnic cultural landscape. The disorderly development of the sports tourism field, new projects will not be in harmony with the original style of the scenic spot, and even change or destroy the original history, culture and atmosphere of the tourism area. The logos and advertisements of the sports tourism field will also cause local humanities and changes in the geography. The domestic waste generated by athletes and spectators causes white pollution and, to varying degrees, causes long-term environmental pollution to the local area. Noise around sports facilities, excessive lighting, and illegal parking has caused the deterioration of the living environment of residents around sports facilities. Therefore, the model must pay more attention to the construction of the human environment while governing the geological ecology. The construction of the sports tourism field broke the ecological balance of the local natural system, increased the pollution and destruction of the original ecological environment, and affected the traditional cultural landscape. Tourism science is an interdisciplinary subject with expertise in application and tourism environmental protection involves a wide range of disciplines. Therefore, in the development and development of scenic spots, multi-disciplinary and in-depth investigation and research should be carried out in order to make more scientific research on tourism (Mert, 2019).
The analysis based on the perspective of geological ecology can comprehensively, objectively and accurately analyze and study the specific reality of a business. It lists advantages, disadvantages, opportunities, threats and other factors closely related to the research object through investigation and summary, and then the various factors are matched with each other and arranged in the form of a matrix, and finally analyzed with the thought of system analysis, so as to obtain a series of conclusions with certain suggestions and decision-making properties. The traditional sports tourism development model basically starts from the perspective of business development and management, but ignores the combination of human leisure experience and inner needs with ecological protection, which is the foothold of this research. Sports tourism is a new form of tourism, and its development time is very short, so the exact concept of it is not perfect at present. Different researchers have studied the development goals, development conditions, functions and principles of sports tourism and what tourists should bear. There are different understandings and definitions based on obligations, activity forms, etc., but generally speaking, it is generally believed that sports tourism is based on a good ecological environment and based on geological ecological ideas to enable tourists to enjoy a form of tourism for the purpose of environment, understanding and protecting the environment.
4.2 Functional integration of sustainable development
Ecotourism advocates enjoying and caring for nature, and reflects the harmony and unity of man and the environment and this shows that the development of ecological tourism depends on the environment. At the same time, improper development of ecological resources also restricts the development of ecological tourism. The geological ecological evaluation can determine the development limit of tourism activities by calculating the regional environmental capacity, and limit the increase in environmental load caused by development activities within the environmental carrying capacity. Through analysis of development and construction activities, the regional environmental air, water environment, acoustic environment, and ecological effects can be determined. Environmental and landscape impacts can determine the environmental protection and preventive measures that should be taken to ensure that all development and construction activities in the sports tourism project area meet the requirements of the construction project environmental protection regulations and environmental impact assessment technical guidelines (Fig. 5). On the basis of in-depth research on tourism resources and the current economic and social development, ecological science studies the development of sports tourism resources and the dynamic management of ecological environmental protection from the changing laws of time and space, and formulates realistic, scientific and reasonable sports tourism development planning. The sustainable development model needs to adhere to the principle of protection first, do a good job in the environmental impact assessment of tourism planning, ensure that the environmental capacity of tourists in sports tourist attractions is reasonably determined, various ecological resources are rationally utilized, and special protection measures for various environmental elements are clearly implemented.
Functional integrations for substantial development of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology.
Sports tourism is a highly interactive way of travel between man and nature and the closest relationship between man and nature and outdoor sports tourism often takes the natural ecological environment as the carrier. Therefore, the harmonious coexistence of sports tourism development and geological ecological protection is the basis and prerequisite for the sustainable development of sports tourism. The sustainable development of sports tourism is not only for the needs of human survival and the sustainable development of society, but also for the sustainable development of sports tourism. Being close to nature is the natural instinct formed by human beings in the long-term evolutionary process, people's participation in sports experience in nature is a return of human nature, and it is the strength and spirituality of human beings in their own perceptual life (Carius and Job, 2019). It can be said that it is the human attachment to the natural landscape and green that leads to the emergence of sports tourism behavior, and the loss of green means the termination of sports tourism behavior. Tourists should respect the customs, traditions and religions of the host group as well as local taboos, scenic spots and sacred sites, protect local animals, plants and other natural resources, and show the greatest understanding of the customs, beliefs and behaviors of the host group. They show the greatest respect for their natural and cultural heritage, and avoid showing the economic, social and cultural differences between them and the local people.
Sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology should make full use of the advantages of local wild herbs, such as rapid soil fixation, fast growth, strong resistance, low cost, and less investment in manual management, for slope protection, which is the best way to maintain water and soil, and green and beautify. Whether from the perspective of the supply of sports tourism resources or the perspective of tourism consumption, geological ecological construction must be carried out on the effective integration and optimization sports tourism resources. Different forest types, tree species, and different types of forests should be used and leaf shape, leaf color, textured trees and abundant ground cover create a forest landscape with rich layers and obvious seasonal changes (Malchrowicz-Mośko et al., 2019). To fundamentally solve the various unhealthy ecological environment problems arising from the construction of ski resorts and skiing sports, it is necessary to strengthen environmental protection education, popularize ecological knowledge, and use various publicity and education methods to improve tourists’ environmental awareness and sustainable development awareness. In addition, the development of sports tourism involves all stakeholders to promote the sustainable development of sports tourism areas. In order to ensure the normal progress of sports tourism, it is necessary to implement sports tourism management mechanisms and government governance models to regulate corporate and individual behaviors and ensure the balance of interests of all tourism stakeholders.
5 Discussions
5.1 Relationship between sports tourism and geological ecological capacity
The original ecological tourism environmental problems refer to the ecological tourism environmental problems caused by the effects of nature, including the ecological tourism resources and environmental damage caused by natural disasters and the deterioration of ecological tourism resources and environmental quality caused by natural factors (Govindan et al., 2016). The secondary tourism ecological environmental problems refer to the destruction, pollution and value reduction of ecological tourism resources and the environment caused by unreasonable tourism activities, production, and life. It includes ecological tourism resources and the environment caused by the destruction of ecological tourism resources and geological ecology caused by unreasonable activities of tourism operators, managers and tourists, waste, waste water, and waste gas. For environmental science, its overall benefits range from 43 % to 72 % with an average of 58 %; for sustainable development, that range from 55 % to 79 % with an average of 68 % (Fig. 6). Environmental capacity, also known as environmental carrying capacity, refers to the maximum amount of human activities that can be accommodated in a certain area under certain conditions and conditions during a certain period of time without damage to the ecological environment of a certain area. There are many measures to control the flow of tourists, such as implementing ticket price fluctuations, issuing capacity control announcements emergency measures to evacuate tourists when there are too many tourists, and temporary closure of designated areas.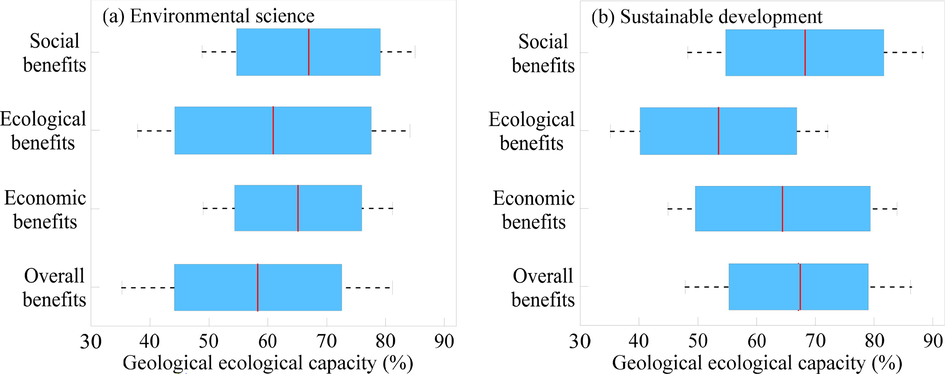
Relationship between sports tourism benefits and geological ecological capacity of environmental science (a) and sustainable development (b).
Ecological sports tourism includes multiple levels of consumer experience and the participation of multiple market actors, covering all market links of demand, supply, intermediary, and support systems. As a form of experience economy, the essence of the supply–demand relationship of ecological sports tourism is to realize the use value of sports tourism services. Ecological sports tourism is an important way for the construction of ecological civilization, which realizes the sustainable use of natural and sports tourism resources and leaves green mountains and waters for future generations. It is a historical and realistic responsibility with contemporary people as the main body and it is also the development of sports tourism. Ecological sports tourism is to incorporate the economic system into the ecological economic form of the ecosystem, to achieve a high degree of unification and overall development of the three major benefits of economy, society and ecology, emphasize the coordinated adaptation of resource development and the ecological environment, and focus on the integrity and system of the development of sports tourism. The nature, strategy and long-term nature are in line with the long-term interests of the development of human society. Ecological sports tourism is essentially a leisure activity that is close to nature and pursues sports cultural experience. Therefore, ecology can be regarded as the inherent requirements for the healthy and sustainable development of sports tourism.
The environmental capacity of sports tourism is a conceptual system, including the psychological capacity of sports tourism, the capacity of sports tourism resources, the ecological capacity of sports tourism, the economic development capacity of sports tourism, and the regional social capacity of sports tourism. Even if it is the same sports tourism destination, if the nature of the sports tourism destination, that is, the type of sports tourism activities it bears, changes, the sports tourism capacity value will also change. Sports tourism capacity is the basic factor that determines the amount of sports tourism activities that can be accommodated in a sports tourism area. As a management tool, it can not only avoid damage to sports tourism destinations, but also ensure the quality of experience of sports tourists (Chow, 2018). The development and protection of sports tourism resources is a concentrated expression of sustainable development in sports tourism, and it is also a necessary prerequisite for the relationship between sports tourism and the environment. The relationship between development and protection runs through the entire development process of the sports tourism industry, and has become increasingly important with the vigorous development of the sports tourism industry. Of course, the general survey of regional sports tourism resources should also be carried out as soon as possible to develop an indeterminate basis for the entire large-region sports tourism to facilitate comprehensive management, to find out the comparative advantages of the specific regional sports tourism industry through vertical and horizontal comparisons, and to determine the environmental capacity of sports tourism.
5.2 Approaches for sustainable development of sports tourism
The development of the sports tourism industry involves many subjects and many related industries and supporting links, and how to effectively chain these related subjects and links and make the composition of the whole play the most effective is related to the overall benefits of the sports tourism industry and development prospects. The concept of sustainable development needs to start with differentiated marketing strategies and thinking, and develops distinctive sports tourism products and services based on the segmentation of the needs of the sports tourism market. For environmental science, the resource integration of sports facilities decrease from 95 % to 66 % when geological ecological capacity range from 40 % to 90 %; for sustainable development, that of sports facilities decrease from 91 % to 59 % when geological ecological capacity range from 40 % to 90 % (Fig. 7). Due to the lack of innovation in sports tourism products and services in the development of the sports tourism industry, the differences and characteristics of products and services in the current sports tourism market are gradually reduced, and the homogeneity of products and services in different sports tourism market segments is becoming more and more serious. Due to the lack of considerations from the upstream and downstream related business entities and business links of the industry chain, the development planning and industrial structure layout of the sports tourism industry lacks macroscopic strategic planning and the ability to control the development trend of the predictive ability of sports tourism industry.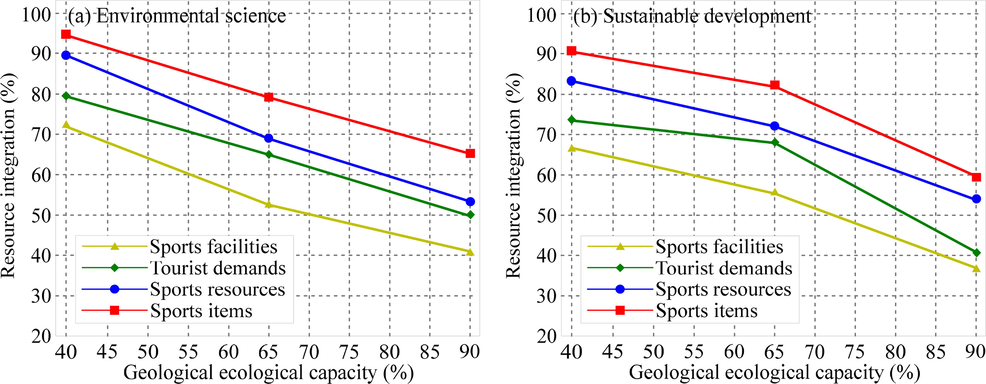
Relationship between resource integration and geological ecological capacity of five sports tourism factors for environment science (a) and sustainable development (b).
The abundance and development of sports tourism resources directly affect the prosperity and development of sports tourism. Sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology should be adapted to local conditions, combined with terrain, avoiding straight-line stiff forest margins, geometric blocks and bands, and fully reflecting the richness of forest landscapes. Due to restrictive factors such as administrative divisions and local interest competition in sports tourism environmental sciences, fragmented management has caused disorderly competition and repeated construction of sports tourism between regions to varying degrees (Fig. 8). The integration and optimization of sports tourism resources are mainly the investigation and evaluation of the integrity of sports tourism resources in and adjacent areas, including the selection of integration modes, the formulation of optimization strategies, and the overall construction of marketing and operations (Karahan and Davardoust, 2020). The integration and optimization of sports tourism resources can promote the overall, systematic and comprehensive coordination of the development of sports tourism resources in small towns. According to the overall goal of geological and ecological development, market positioning, and the supply and demand situation of the sports tourism market, the overall planning, systematic development and linkage development in the region will make various relevant resource elements a whole with a unified function. With the core of enhancing the competitiveness of the small town sports tourism industry, this is to maximize the market value of the small town sports tourism resources and maximize the overall benefits.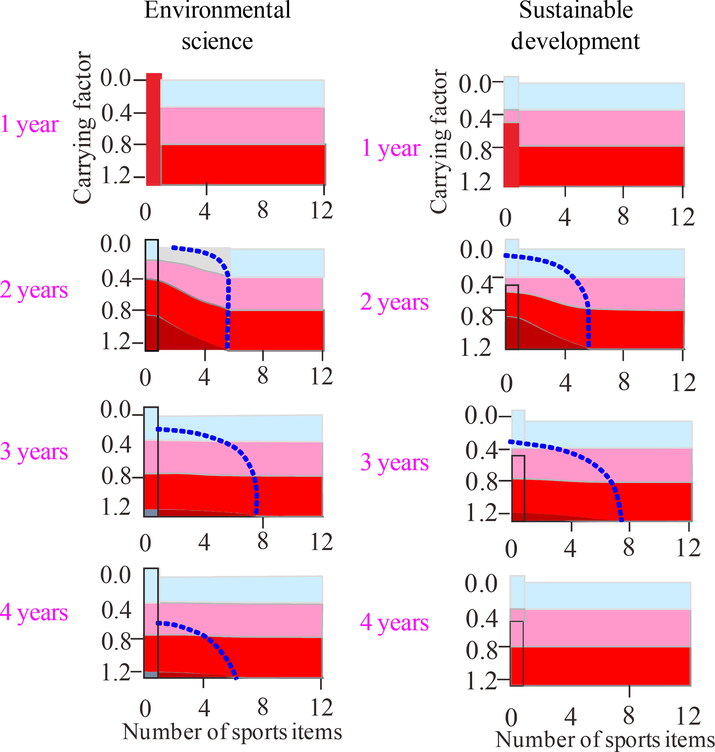
Evolution of geological carrying factor with the number of sports items at 1–4 tourism years in environment science (a) and sustainable development (b).
As a sustainable development model with special protection responsibility for natural and cultural tourism resources, ecological sports tourism can realize the sustainable use of sports tourism resources by reducing environmental pressure. It is an inevitable choice to realize the sustainable development of sports tourism by protecting the integrity of tourism resources and culture, balancing economic interests, and realizing mutual benefit sharing and fairness. Therefore, sports tourism must follow the laws of ecology in planning, development, utilization, and management, with the concept of sustainable development as the guiding ideology, study the carrying capacity of sports tourism, control the ecological capacity, ensure the beauty of the ecological environment, and maintain the resources of sports tourism. Its protection is embodied in promoting a virtuous cycle of the natural ecological environment; promoting the protection of organisms, especially rare and endangered organisms (Usmanova, 2022). The prerequisite for the sustainable development of tourism is the sustainable use of tourism resources and its primary goal is development and the foundation is the sustainable use of tourism resources and environmental protection. It also includes promoting the protection of water bodies and the treatment of water pollution, and has a good protective effect on the atmospheric environment and geological landforms. Only by maintaining long-term coordination between the development of sports tourism and the ecological environment and achieving the overall dynamic harmony between man and nature, between man and man, and between man and society, can the sustainable development of sports tourism be finally realized.
6 Conclusions
This paper conducted the model construction of environmental science for sports tourism, analyzed the optimization strategy of environmental science for sports tourism, constructed the environmental science of sports tourism based on geological ecology, performed the resource integration of sustainable development for sports tourism, proposed the functional integration of sustainable development for sports tourism, explored the sustainable development of sports tourism based on geological ecology, and finally discussed the relationship between sports tourism and geological ecological capacity and the achieving approaches for sustainable development of sports tourism. Sports tourism capacity is the basic factor that determines the amount of sports tourism activities that can be accommodated in a sports tourism area. As a management tool, it can not only avoid damage to sports tourism destinations, but also ensure the quality of experience of sports tourists. Sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology should make full use of the advantages of local wild herbs, such as rapid soil fixation, fast growth, strong resistance, low cost, and less investment in manual management, for slope protection, which is the best way to maintain water and soil, and green and beautify. The original natural conditions should be used as much as possible to avoid large-scale changes to the local topography, vegetation, and hydrology. The development and protection of sports tourism resources is a concentrated expression of sustainable development in sports tourism, and it is also a necessary prerequisite for the relationship between sports tourism and the environment. This study did not differentiate the environmental science and sustainable development of sports tourism which needs further research. The study results show that the environmental science and sustainable development of sports tourism based on the perspective of geological ecology can ecologically and organically combine sports activities and tourism activities in accordance with scientific and reasonable concepts, develop various sports that can satisfy tourist demands, and can achieve ecological, economic and social benefits of ecological sports tourism.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Geography and environment-analysis of indicators of sustainable development of tourism. Int. J. Cognitive Res. Sci. Eng. Education. 2017;5(1):131.
- [Google Scholar]
- Community involvement and tourism revenue sharing as contributing factors to the UN Sustainable Development Goals in Jozani-Chwaka Bay National Park and Biosphere Reserve, Zanzibar. J. Sustain. Tourism. 2019;27(6):826-846.
- [Google Scholar]
- Evaluation of the recreational potential of Kutahya Urban Forest. Fresen. Environ. Bull.. 2018;27(5):2629-2634.
- [Google Scholar]
- Assessment and improvement of wetlands environmental protection plans for achieving sustainable development. Environ. Res.. 2019;169:280-296.
- [Google Scholar]
- Mangrove management for climate change adaptation and sustainable development in coastal zones. J. Sustain. For.. 2018;37(2):139-156.
- [Google Scholar]
- Landmarks in relation to sustainable development and the growing environmental emphasis in sport mega-events. PASOS: Revista de Turismo y Patrimonio Cultural. 2019;17(1):179-192.
- [Google Scholar]
- Sustainable development and exploitation of semi-mountainous area in Greece. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev.. 2016;7(6):473.
- [Google Scholar]
- Residents’ perception of the impact of sports tourism on sustainable social development. Sustainability. 2022;14(3):1232.
- [Google Scholar]
- Greenways for rural sustainable development: an integration between geographic information systems and group analytic hierarchy process. Land Use Policy. 2016;50:429-440.
- [Google Scholar]
- Participation in active sport tourism: impact assessment of destination involvement and perceived risk. J. Sport Tourism. 2022;26(2):101-123.
- [Google Scholar]
- Evaluation of vernacular architecture of Uzundere District (architectural typology and physical form of building) in relation to ecological sustainable development. J. Asian Architecture Build. Eng.. 2020;19(5):490-501.
- [Google Scholar]
- Sustainable development of Turkey: deployment of geothermal resources for carbon capture, utilization, and storage. Energy Sources Part A: Recovery, Utilization Environ. Effects. 2019;41(14):1739-1751.
- [Google Scholar]
- “Because we don’t want to run in smog”: Problems with the sustainable management of sport event tourism in protected areas (a case study of National Parks in Poland and Slovakia) Sustainability. 2019;11(2):325.
- [Google Scholar]
- Environmental impact assessment in climbing activities: a new method to develop a sustainable tourism in geological and nature reserves. Geoheritage. 2020;12(1):1-16.
- [Google Scholar]
- Sport ecology: conceptualizing an emerging subdiscipline within sport management. J. Sport Manag.. 2020;34(6):509-520.
- [Google Scholar]
- Contribution to sustainable development: Re-development of post-mining brownfields. J. Clean. Prod.. 2019;240:118212
- [Google Scholar]
- The anthropocenic imaginary: political ecologies of tourism in a geological epoch. J. Sustain. Tour.. 2019;27(4):421-435.
- [Google Scholar]
- From piecemeal to holistic: introducing sustainability science in Indian Universities to attain UN-Sustainable Development Goals. J. Clean. Prod.. 2020;247:119133
- [Google Scholar]
- Assessing ecotourism potential for sustainable development of coastal tourism in qeshm island, iran. Eur. J. Geogr.. 2016;7(4):53-66.
- [Google Scholar]
- Linking tourism to the sustainable development goals: A geographical perspective. Tour. Geogr.. 2018;20(2):341-342.
- [Google Scholar]
- Sport tourism as a sport and form of activity. Eur. J. Innovation Nonformal Education. 2022;2(1):212-214.
- [Google Scholar]
- The impact of marine tourism resources development on sustainable development of marine economy. J. Coast. Res.. 2019;94(SI):589-592.
- [Google Scholar]







