Translate this page into:
Electro-optical and charge injection investigations of the donor-π-acceptor triphenylamine, oligocene–thiophene–pyrimidine and cyanoacetic acid based multifunctional dyes
⁎Corresponding author at: Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King Khalid University, Abha 61413, P.O. Box 9004, Saudi Arabia. Tel.: +966 172418632; fax: +966 172418426. irfaahmad@gmail.com (Ahmad Irfan)
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
This article was originally published by Elsevier and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Peer review under responsibility of King Saud University.
Abstract
The corner stone of present study is to tune the electro-optical and charge transport properties of donor-bridge-acceptor (D-π-A) triphenylamine (TPA) derivatives. In the present investigation, an electron deficient moiety (pyrimidine), electron-rich moiety (thiophene) and oligocene (benzene, naphthalene, anthracene, tetracene and pentacene) have been incorporated as π-spacer between the donor TPA unit and cyanoacetic acid acceptor and anchoring group. The elongation of bridge usually affects the energy levels, i.e., higher the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) while lower the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) thus reduces the HOMO–LUMO energy gap. The lowered LUMO energy levels of cyano-{2-[6-(4-diphenylamino-phenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-tetraceno[2,3-b]thiophen-8-yl}-acetic acid (TPA-PTT4) and cyano-{2-[6-(4-diphenylamino-phenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-pentaceno[2,3-b]thiophen-9-yl}-acetic acid (TPA-PPT5) dyes revealed that electron injected from dye to semiconductor surface might be auxiliary stable resulting in impediment of quenching. The broken co-planarity between the π-spacer conceiving LUMO and the TPA moiety would help to impede the recombination process. Moreover, it is expected that TPA derivatives with the tetracenothiophene and pentacenothiophene moieties as π-bridge would show better photovoltaic performance due to lowered LUMO energy level, higher electronic coupling constant, light harvesting efficiency and electron injection values.
Keywords
Photovoltaics
Triphenylamines
Density functional theory
Electro-optical properties
Charge transport properties
1 Introduction
The compounds with the π-backbone showed prominent opto-electronic and charge transport properties in different high-tech fields, e.g., sensors (Niu et al., 2006), organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) (Makoto Satsuki and Sadaharu Suga, 2007), organic field effect transistors (OFET) (Marks and Hersam, 2015) and photovoltaics (Chambon et al., 2013). Previously, numerous inorganic materials were studied with respect to the solar cell (Green et al., 2012) and to sense the humidity (Traversa et al., 1996; Li et al., 2004). The traditional technology (silicone), have environmental and economic issues. Moreover, metal oxides are being used in the film making of dye-sensitized solar cells, (DSCs) (O’Regan and Gratzel, 1991) and humidity sensors (Suri et al., 2002; Hsu et al., 2014). Nowadays, organic materials are being used due to their low cost, light weight, structural flexibility and fabrication simplicity. Finally, the organic dyes are favorite contenders for power conversion and sensing applications.
The power conversion efficiency (PCE) has been observed as 13% when using the porphyrin dye (Mathew et al., 2014) showing a competitive and potential renewable power generation technology. In DSCs, the dye sensitizer is a key component which has been widely designed and investigated to enhance the PCE that also harvests solar photons and starts charge separation from the excited state of the sensitizer into the conduction band of the semiconductor through photoinduced electron transfer (Bessho et al., 2009; Han et al., 2012).
Molecular engineering to model/design efficient dyes play a vital role in tuning the electro-optical and charge transport properties, i.e., light excitation should accompanyelectron injection from the light-harvesting unit toward the anchoring group. This can be attained by incorporating the strong conjugation between the donor moieties and anchoring groups as well as decent electronic coupling between the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) of the dye and conduction band of the semiconductor. The PCE can be improved by diminishing the aggregation of the sensitizer on the semiconductor surface. Moreover, “bulk heterojunction” (BHJ) solar cells are also gaining significant attention (Hoppe and Sariciftci, 2006). The organic π-conjugated materials are being used in DSCs, BHJ solar cells and humidity sensors.
Triphenylamine (TPA) has revealed promising properties as donor (Hagberg et al., 2007; Liang and Chen, 2013) and its propeller shape can suppress the dye aggregation (Bonhôte et al., 1999). Cyanoacetic acid showed promising characteristics as stable anchoring and strong acceptor groups (Chen et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2015). Usually, π-spacer can directly influence the energies of the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO), LUMO, absorption spectrum, and the charge separation upon photoexcitation of the sensitizer (Haid et al., 2012). Thus the choice of a suitable π-spacer is very crucial. It has been proven that thiophene would be a good constitutional unit which can increase the light harvesting efficiency and charge transport properties (Zhang et al., 2009; Tian et al., 2010). Similarly, oligocenes are also being used as proficient π-spacers to tune the electro-optical and charge transport properties (Liu et al., 2014).
Quantum chemical calculations are prevailing tools (Goedecke et al., 2012) which provide guidelines for the organized and rational tuning of the dyes (Pastore et al., 2010a,b). It is well-known that density functional theory (DFT) and Time Dependent DFT (TD-DFT) are reasonable methods to calculate electronic structures, electronic excitations, predict the electro-optical and charge transport properties of organic chromophores with adequate accurateness (Cave and Castner, 2002; Persson et al., 2006; Pastore et al., 2010b). We designed systematically five new TPA derivatives to tune the electro-optical properties and dye’s photoabsorption. In newly designed donor-bridge-acceptor derivatives TPA acts as electron donor, oligocenothiophene–pyrimidine as π-spacer and cyanoacetic acid as an electron acceptor and anchoring group, i.e., cyano-{2-[6-(4-diphenylamino-phenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-benzo[b]thiophen-5-yl}-acetic acid (TPA-PBT1), cyano-{2-[6-(4-diphenylamino-phenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-naphtho[2,3-b]thiophen-6-yl}-acetic acid (TPA-PNT2), cyano-{2-[6-(4-diphenylamino-phenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-anthra[2,3-b]thiophen-7-yl}-acetic acid (TPA-PAT3), cyano-{2-[6-(4-diphenylamino-phenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-tetraceno[2,3-b]thiophen-8-yl}-acetic acid (TPA-PTT4) and cyano-{2-[6-(4-diphenylamino-phenyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-pentaceno[2,3-b]thiophen-9-yl}-acetic acid (TPA-PPT5), see Fig. 1.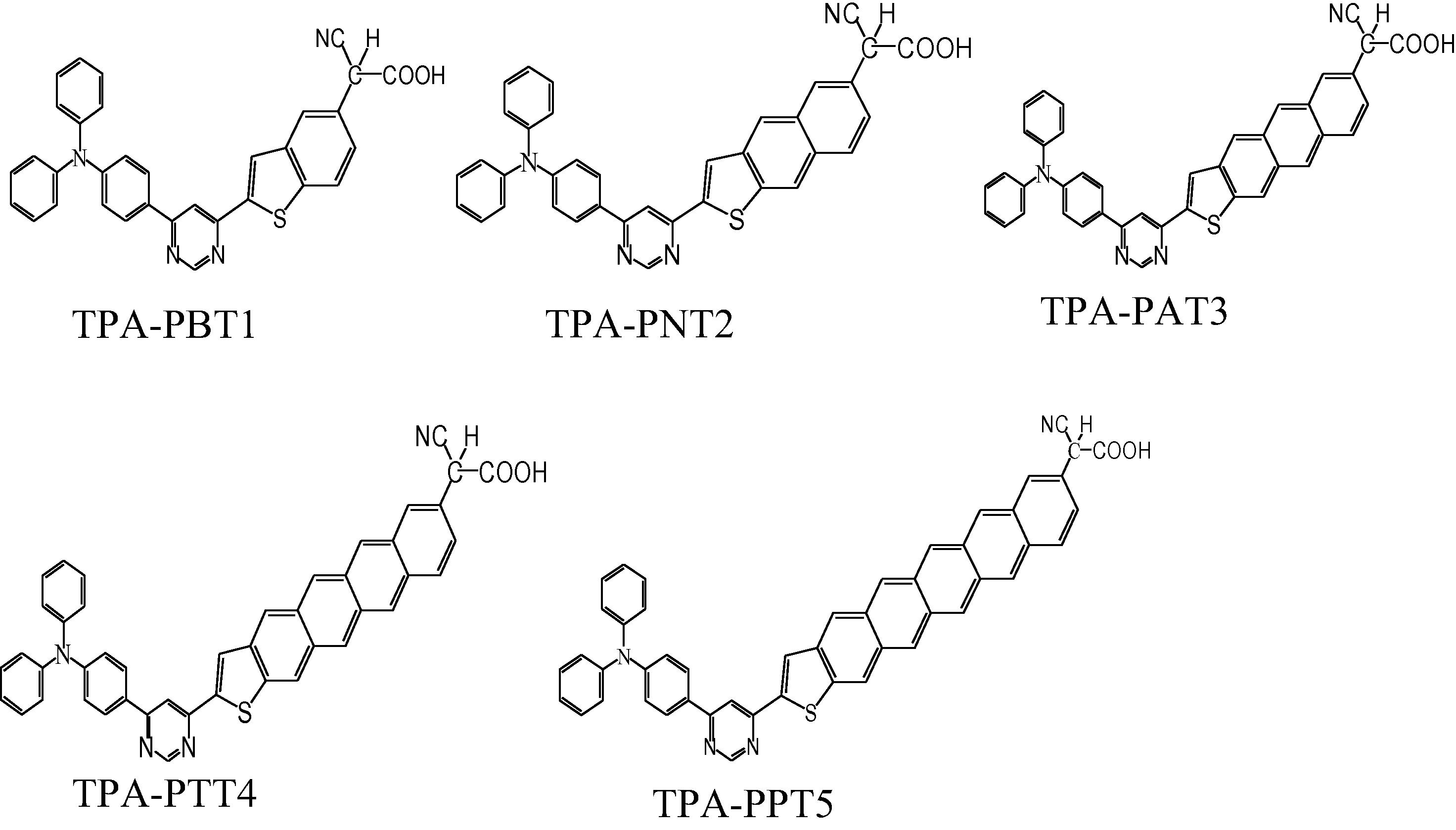
The donor-bridge-acceptor systems investigated in the present study.
We have studied the energy levels and distribution patterns of the frontier molecular orbitals (HOMO, LUMO), excitation energies, oscillator strengths, electronic coupling constants, electron injection, light harvesting efficiencies and structure–properties relationship. The conclusions drawn from quantum chemical calculations are appreciated as guidelines for the synthesis of innovative proficient dyes (Casanova et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2012).
2 Computational details
In previous studies it has been shown that DFT is good method to optimize the ground state geometries, particularly B3LYP/6-31G∗∗ level of theory is reasonable and precise choices for TPA sensitizers. Preat and co-workers optimized the ground state geometries of TPA based sensitizers at B3LYP/6-31G∗∗ level and found it to be a rational approach then they studied the charge transport properties (Preat et al., 2010). Moreover, in another study, they investigated the basis set effect on the properties of interests and did not find a significant effect on bond lengths (Preat et al., 2009). The structural and electronic properties of TPA based dye “2-cyano-5-(4-(phenyl(4-vinylphenyl)amino)phenyl)penta-2,4-dienoic acid” (TC4) were studied at B3LYP/6-31G∗∗ level which reproduced the experimental data successfully (Xu et al., 2008). Furthermore, TDDFT (Sun et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2008) TD-CAM-B3LYP/6-31G∗∗ level has been adopted to shed light on the light harvesting efficiencies (LHE), absorption spectra, oscillator strengths and excitation energies of TPA based sensitizers. Thus in the present study, the ground state geometries were optimized at B3LYP/6-31G∗∗ level of theory then excitation energies and oscillator strengths were computed by adopting the TD-CAM-B3LYP/6-31G∗∗ level of theory. All calculations were performed by G09 software (Frisch et al., 2009).
Generally Marcus theory (Eq. (1)) is used to shed light on the charge transfer rate (Marcus, 1993; Matthews et al., 1996; Hilgendorff and Sundström, 1998; Pourtois et al., 2002; Hsu, 2009),
The ΔGinject. and have been evaluated using Eqs. (4) and (5).
The LHE can be evaluated as (Nalwa, 2001):
The efficiency (
) of solar cells can be determined by using the following equation
3 Result and discussion
3.1 Electro-optical properties
In Fig. 2, we have illustrated the charge density distribution patterns of the ground state highest occupied molecular orbitals and lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals which contribute in the transitions, e.g., HOMOs (H), HOMOs−1 (H−1), HOMOs−2 (H−2), LUMOs (L), LUMOs+1 (L+1) and LUMOs+2 (L+2) of five TPA based sensitizers. In TPA-PBT1, a major transition has been observed H → L in which HOMO is delocalized on the TPA moiety whereas LUMO is localized on the benzothiophene and pyrimidine units. The absorption wavelength (λa) for this transition has been observed as 337 nm with the oscillator strength (f) 1.0374. In TPA-PNT2, two significant transitions have been noticed H−1 → L and H−1 → L+1 with the f 0.6871 and 0.7902 showing at the λa 349 and 274 nm wavelengths. In this sensitizer, the charge density in HOMO−1, HOMO, and LUMO is distributed on naphthothiophene, TPA and naphthothiophene pyrimidine cores, respectively while in LUMO+1, most of the charge is distributed on pyrimidine and phenyl rings of the TPA while some charge is localized on the naphthothiophene moiety. In TPA-PAT3, two significant transitions have been observed H → L and H−1 → L with the f 0.1465 and 1.2423 showing the λa 413 and 341 nm. In this dye, the charge density in HOMO−1 and HOMO is distributed on the entire dye while in LUMO on anthrathiophene units. In TPA-PTT4, two significant transitions have been observed H → L and H−2 → L with the f 0.0866 and 1.2674 showing at the λa 499 and 354 nm wavelengths. In this dye, the charge density in HOMO is distributed on tetracenothiophene while HOMO−2 and LUMO on tetracenothiophene and pyrimidine. In TPA-PPT5, two significant transitions have been observed H → L and H → L + 4 with the f 0.0698 and 1.7681 showing at the λa 599 and 297 nm wavelengths. In this dye, the charge density in HOMO is distributed on pentacenothiophene, LUMO on pentacenothiophene and pyrimidine and LUMO+4 on pentacene and acceptor moiety.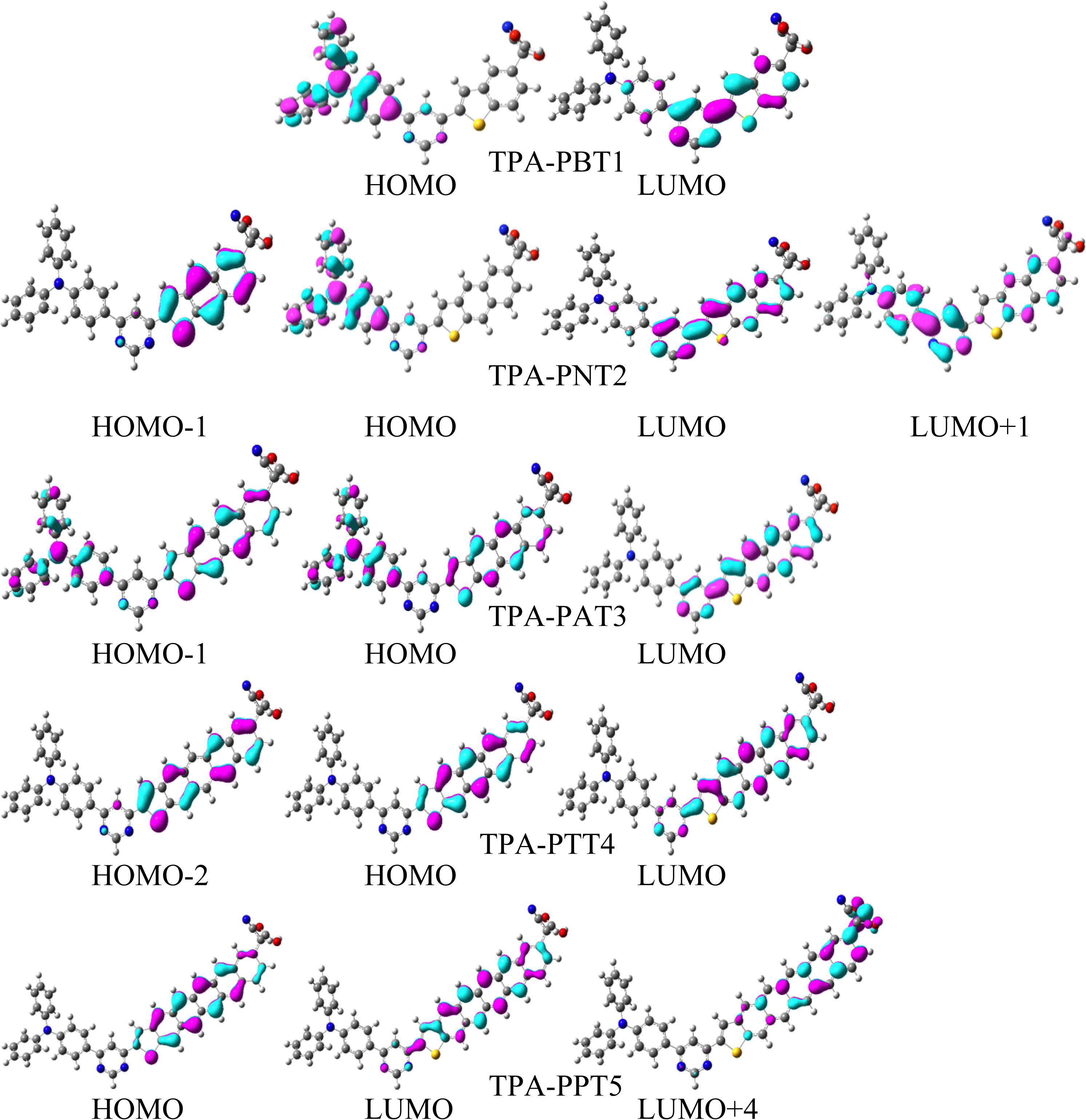
The charge density distribution of the frontier molecular orbitals (0.035 contour value) of triphenylamine based dye at the B3LYP/6-31G∗∗ level of theory.
In Table 1, we have tabulated the computed HOMOs energies (EHOMOs), LUMOs energies (ELUMOs) and energy gap (Eg) of five TPA-based sensitizers at B3LYP/6-31G∗∗ level of theory. The trend of the HOMO energies (EHOMO) is TPA-PPT5 > TPA-PTT4 > TPA-PAT3 > TPA-PBT1 > TPA-PNT2, whereas, LUMO energies (ELUMO) is TPA-PBT1 > TPA-PNT2 > TPA-PAT3 > TPA-PTT4 > TPA-PPT5 while HOMO–LUMO energy gaps (Eg) is TPA-PBT1 > TPA-PNT2 > TPA-PAT3 > TPA-PTT4 > TPA-PPT5. We have observed that by elongating the bridge Eg usually decreases. The smaller Eg of TPA-PNT2, TPA-PAT3, TPA-PTT4 and TPA-PPT5 than TPA-PBT1 show that DSCs performance of these sensitizers would be greater than the later one. Considerably lowered LUMO energy levels would not only enhance the electron injection ability but also make such sensitizers unsusceptible to oxidation. The smaller ELUMO of TPA-PNT2, TPA-PAT3, TPA-PTT4 and TPA-PPT5 sensitizers also showed that injected electrons might be supplementary stable, which would result in hindering the quenching. Moreover, the trend of the Eg is in good agreement with λa. A significant red shift has been observed by increasing the conjugation/bridge elongation, i.e., 12, 76, 162 and 262 nm form TPA-PNT2, TPA-PAT3, TPA-PTT4 and TPA-PPT5 compared to the TPA-PBT1 revealing efficient visible light sensing/absorbing sensitizers. Moreover, it is also expected that these dyes can be used as sensors having the sensing aptitudes of metal ions in the UV–Visible wavelengths. Δ
= relative electron injection ΔGinject(TPAdye)/ΔGinject(TC4).
Systems
ΔGinject
ƒ
LHE
Δ
|VRP|
λa
Transition
aTC4
−1.71
5.22
2.29
2.93
1.5800
0.974
1.00
0.860
423
H → L
TPA-PBT1
−2.56
5.12
1.44
3.68
1.0374
0.908
1.50
1.280
337
H → L
TPA-PNT2
−2.40
5.15
1.60
3.55
0.6871
0.794
1.40
1.200
349
H-1 → L
−3.38
5.15
0.62
4.53
0.7902
0.838
1.98
1.690
274
H-1 → L + 1
TPA-PAT3
−1.88
5.12
2.12
3.00
0.1465
0.286
1.10
0.940
413
H → L
−2.29
5.12
1.71
3.41
1.2423
0.943
1.34
1.145
341
H-1 → L
TPA-PTT4
−1.61
4.87
2.39
2.48
0.0866
0.181
0.94
0.805
499
H → L
−2.63
4.87
1.37
3.50
1.2674
0.946
1.54
1.315
354
H-2 → L
TPA-PPT5
−1.46
4.61
2.54
2.07
0.0698
0.148
0.85
0.730
599
H → L
−3.56
4.61
0.44
4.17
1.7681
0.983
2.08
1.780
297
H → L + 4
3.2 Electron injection
The ΔGinject, ΔGrinject, , , , LHE and |VRP| have been tabulated in Table 1. In investigated derivatives, the |VRP| and ΔGrinject are superior as compared to the TC4. Two important excitations have been observed in all derivatives except TPA-PBT1. The ΔGinject and |VRP| for TPA-PBT1 has been observed at −2.56 and 1.28. The ΔGinject (|VRP|) of TPA-PNT2 for first and second transitions have been observed at −2.40 and −3.38 (1.20 and 1.69), respectively. In TPA-PAT3, the ΔGinject (|VRP|) for first and second transitions have been observed at −1.88 and −2.29 (0.940 and 1.145), respectively. In TPA-PTT4, the ΔGinject (|VRP|) for first and second transitions have been observed at −1.61 and −2.63 (0.805 and 1.315), respectively. In TPA-PPT5, the ΔGinject (|VRP|) for first and second transitions have been observed at −1.46 and −3.56 (0.730 and 1.780), respectively. All these studied sensitizers have superior ΔGinject and |VRP| compared to TC4 which has the values of −1.71 and 0.86, respectively. The azo dye based triaminopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivative (4b) showed ΔGinject and |VRP| −1.19 and 0.53 at TD-B3LYP/6-31G∗//B3LYP/6-31G∗ level of theory, respectively (Al-Sehemi et al., 2013). The ΔGinject and |VRP| of hydrazone based sensitizers (system5) were found −0.61 and 0.305 at TD-B3LYP/6-31G∗//B3LYP/6-31G∗ level of theory, respectively (Al-Sehemi et al., 2012). In the present study, the ΔGinject and |VRP| of newly designed derivatives reveal that these materials might be proficient sensitizers.
The comprehensive intra-molecular charge transfer has been observed from the donor to the acceptor side. The bridge elongation is favorable to enhance the ΔGinject and |VRP|. The LHE of TPA-PBT1 has been observed as 0.908. By introducing the naphthalene ring as in TPA-PNT2 decreases the LHE to 0.794 and 0.838 for two major excitations. In TPA-PAT3, the LHE has been observed to be 0.286 and 0.943; in TPA-PTT4, 0.180 and 0.946; in TPA-PPT5, 0.148 and 0.983 for two major excitations, respectively. Thus it has been concluded that bridge elongation enhances the LHE and is nicely comparable with the earlier study.
All the studied sensitizers have acidic moieties which are good light harvesting sites as well as being helpful to anchor with the TiO2 surface. These acidic units would also enhance the solubility in solution and reduce the aggregation (Robertson, 2006). It is expected that these sensitizers would be more stable after anchoring on the TiO2 surface. Moreover, acidic ligands would be promising positions to transfer the electrons from dyes to the TiO2 surface. Additionally, it has been studied that the dye which shows high affinity for H2O molecules would lead to the proficient humidity sensor (Azmer et al., 2015). In our studied TPA dyes, the carboxylic group would be the favorable site and shows high affinity for H2O molecules. It is expected that –COOH would be promising position for the humidity sensing.
3.3 Electronic properties
The HOMO and LUMO energies of Si are −5.43 and −3.92 eV (Liu et al., 2008) while TiO2 are −7.40 and −4.20 eV, respectively (Kuo et al., 2008). The successful operation of a photovoltaic device requires a staggered band alignment heterojunction which allocate electrons to transport to the cathode and holes to the anode. By considering the average values both for Si and TiO2, the valance band energy has been found to be−6.41 eV while the conduction band energy is −4.06 eV (Si/TiO2). It is expected that Si/TiO2 as the acceptor would behave as a staggered band alignment heterojunction, see Fig. 3.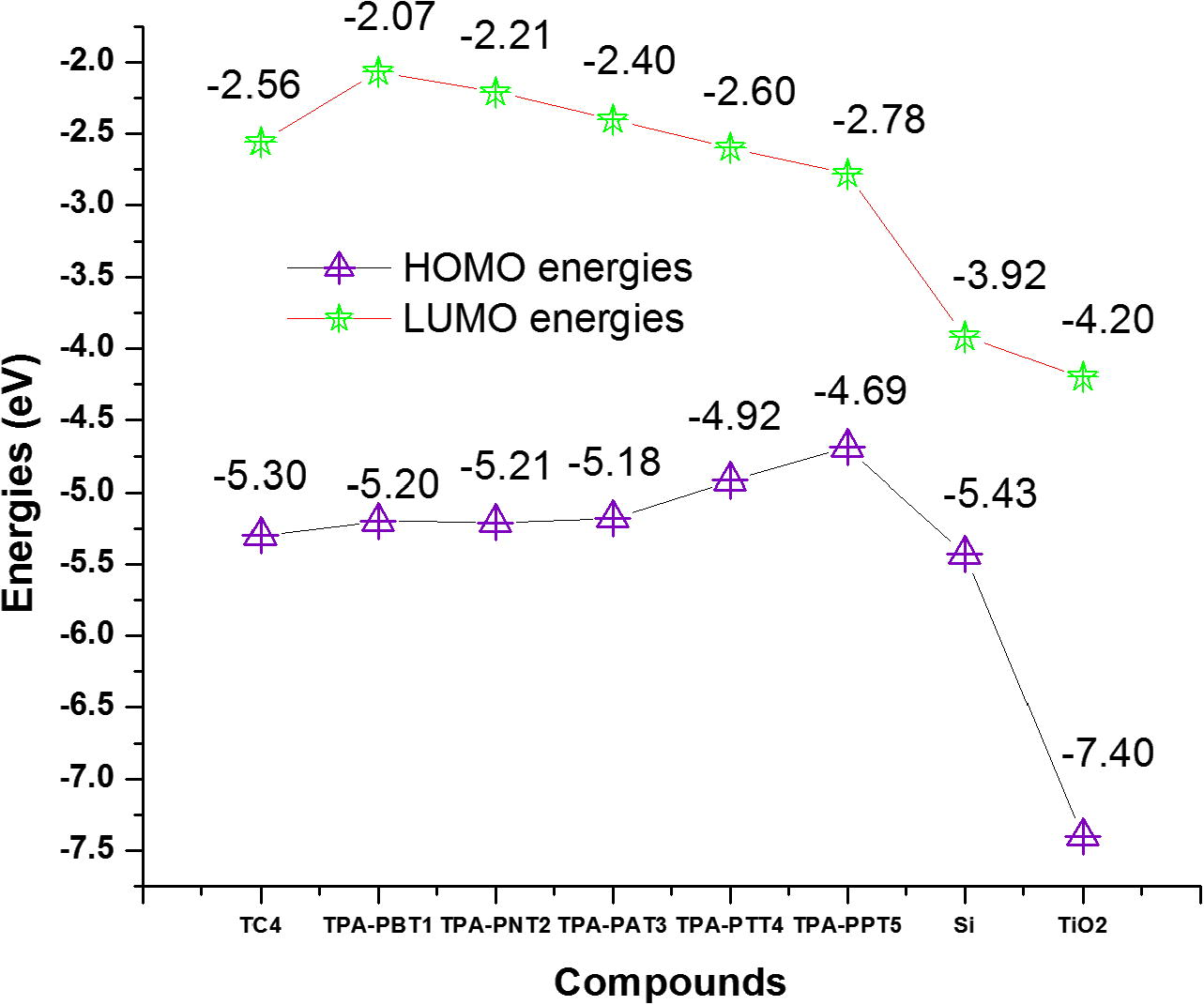
The HOMOs and LUMOs energies of donors and acceptors.
In hybrid solar cells, excitons formed in the donor material are dissociated at the D–A interface. The force essential to overcome the exciton binding energy is provided by the energy level offset of the LUMO of the donor and the conduction band edge of the acceptor material (Wright and Uddin, 2012). We found energy level offset 1.50, 1.99, 1.85, 1.66, 1.46, and 1.28 eV for TC4, TPA-PBT1, TPA-PNT2, TPA-PAT3, TPA-PTT4 and TPA-PPT5, respectively to overcome the exciton binding energy. For dissociation of excitons formed in the acceptor material, the energy offset of the HOMO of the donor and the valence band edge of the acceptor material is required. We found energy level offset to be 1.11, 1.21, 1.20, 1.23, 1.49, 1.72 eV for TC4, TPA-PBT1, TPA-PNT2, TPA-PAT3, TPA-PTT4 and TPA-PPT5, respectively. Scharber and coworkers concluded that Voc is directly proportional to the diagonal band gap of the heterojunction (Scharber et al., 2006), whereas in another study by Yamanari it has been found that there is no linear relationship between the diagonal band gap and Voc (Yamanari et al., 2009). In the present study, the diagonal band gaps for TC4, TPA-PBT1, TPA-PNT2, TPA-PAT3, TPA-PTT4 and TPA-PPT5 have been observed 1.24, 1.14, 1.15, 1.12, 0.86, 0.63 eV, respectively. Thus from these values, we are unable to conclude that either Voc would enhance or reduce the efficiency. But it is understood that Voc is not only the factor which can improve the efficiency. In our previous study, we found the measured Voc 0.53 and 0.60 V for 2-{4-[2-(4-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazino]phenyl}ethylene-1,1,2-tricarbonitrile (dye2) and hydrazone 2-{4-[2-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazino]phenyl}ethylene-1,1,2-tricarbonitrile (dye1) with efficiencies of 3.58% and 2.76%, respectively. The superior efficiency in hydrazone dye2 was observed due to the larger Jsc and FF values (Al-Sehemi et al., 2014). On the other hand, it is expected that higher LHE and ΔGinject would lead to result in efficient devices due to the improved Jsc.
4 Conclusions
Our results exhibited that by elongating the bridge HOMO–LUMO energy gap decreases in triphenylamine derivatives. The smaller energy gaps of TPA-PNT2, TPA-PAT3, TPA-PTT4 and TPA-PPT5 than TPA-PBT1 show that performance of former dyes would be greater than the later one. Considerably lowered LUMO energy level would not only enhance the electron injection ability but also make such dyes unsusceptible to oxidation. The smaller LUMO energies of TPA-PNT2, TPA-PAT3, TPA-PTT4 and TPA-PPT5 sensitizers also showed that injected electrons might be supplementary stable, which would impede the quenching. Bridge elongation improves the electron injection, electron coupling constants and light harvesting efficiencies. The Si/TiO2 as acceptor materials might be favorable for staggered band alignment that would be best for charge transport from donor to acceptor moieties. The co-planarity between the bridge having LUMO and the TPA moiety is broken ensuing a positive charge that may not directly fall to the TiO2 surface, subsequently obstructing the recombination process. The electron injection of 2-cyano-5-(4-(phenyl(4-vinylphenyl)amino)phenyl)penta-2,4-dienoic acid (TC4) was observed to be −1.71. The electron injection of TPA-PBT1, TPA-PNT2, TPA-PAT3, TPA-PTT4 and TPA-PPT5 is 1.50, 1.98, 1.34, 1.54 and 2.08 times superior to TC4. Moreover, the superior electron injection, relative electron injection and electron coupling constants of new designed photosensitizers revealed that these dyes might be proficient as compared to the TC4. It is also expected that higher light harvesting efficiencies and electron injection would improve the short-circuit current density which lead to proficient multifunctional devices.
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the Ministry of higher education, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for their financial support to carry out this research through Grant (PCSED-005-14) under the promising center for sensors and electronics devices (PCSED) at the Najran University.
References
- The DFT investigations of the electron injection in hydrazone-based sensitizers. Theoret. Chem. Acc.. 2012;131(3):1199.
- [Google Scholar]
- The enhanced efficiency to 3.6% based on organic dye as donor and Si/TiO2 acceptor bulk hetero-junction solar cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A. 2014;292:1-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Synthesis, characterization and density functional theory investigations of the electronic, photophysical and charge transfer properties of donor–bridge–acceptor triaminopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine dyes. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc.. 2013;111:223-229.
- [Google Scholar]
- Evidences of hot excited state electron injection from sensitizer molecules to TiO2 nanocrystalline thin films. Res. Chem. Intermed.. 2001;27(4–5):393-406.
- [Google Scholar]
- Humidity dependent electrical properties of an organic material DMBHPET. Measurement. 2015;61:180-184.
- [Google Scholar]
- New paradigm in molecular engineering of sensitizers for solar cell applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc.. 2009;131(16):5930-5934.
- [Google Scholar]
- Long-lived photoinduced charge separation and redox-type photochromism on mesoporous oxide films sensitized by molecular dyads. J. Am. Chem. Soc.. 1999;121(6):1324-1336.
- [Google Scholar]
- Computational study of promising organic dyes for high-performance sensitized solar cells. J. Chem. Theory Comput.. 2010;6(4):1219-1227.
- [Google Scholar]
- Time-dependent density functional theory investigation of the ground and excited states of coumarins 102, 152, 153, and 343. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2002;106(50):12117-12123.
- [Google Scholar]
- Solution-processed bulk heterojunction solar cells based on BF2-hydroxychalcone complexes. Chem. Commun.. 2013;49(34):3555-3557.
- [Google Scholar]
- Theoretical investigation of phenothiazine–triphenylamine-based organic dyes with different π spacers for dye-sensitized solar cells. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc.. 2014;123:282-289.
- [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J, Schlegel, H., et al., 2009. Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT, Gaussian 09, Revision A. 01.
- Spacer separated donor–acceptor complexes [D → C6F4 → BF3] (D = Xe, CO, N2) and the dication [Xe → C6F4 ← Xe]2+. A theoretical study. Inorg. Chem.. 2012;51(21):11259-11265.
- [Google Scholar]
- Solar cell efficiency tables (version 39) Prog. Photovoltaics Res. Appl.. 2012;20:12-20.
- [Google Scholar]
- Tuning the HOMO and LUMO energy levels of organic chromophores for dye sensitized solar cells. J. Org. Chem.. 2007;72(25):9550-9556.
- [Google Scholar]
- Light-induced redox reactions in nanocrystalline systems. Chem. Rev.. 1995;95(1):49-68.
- [Google Scholar]
- Significant improvement of dye-sensitized solar cell performance by small structural modification in π-conjugated donor–acceptor dyes. Adv. Funct. Mater.. 2012;22(6):1291-1302.
- [Google Scholar]
- High-efficiency dye-sensitized solar cell with a novel co-adsorbent. Energy Environ. Sci.. 2012;5(3):6057-6060.
- [Google Scholar]
- Dynamics of electron injection and recombination of dye-sensitized TiO2 particles. J. Phys. Chem. B. 1998;102(51):10505-10514.
- [Google Scholar]
- Morphology of polymer/fullerene bulk heterojunction solar cells. J. Mater. Chem.. 2006;16(1):45-61.
- [Google Scholar]
- The electronic couplings in electron transfer and excitation energy transfer. Acc. Chem. Res.. 2009;42(4):509-518.
- [Google Scholar]
- Rapid synthesis of ZnO dandelion-like nanostructures and their applications in humidity sensing and photocatalysis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process.. 2014;21:200-205.
- [Google Scholar]
- Quantum chemical investigations of electron injection in triphenylamine-dye sensitized TiO2 used in dye sensitized solar cells. Mater. Chem. Phys.. 2013;142(1):238-247.
- [Google Scholar]
- Efficiencies of electron injection from excited N3 dye into nanocrystalline semiconductor (ZrO2, TiO2, ZnO, Nb2O5, SnO2, In2O3) films. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2004;108(15):4818-4822.
- [Google Scholar]
- Ordered bulk heterojunction solar cells with vertically aligned TiO2 nanorods embedded in a conjugated polymer. Appl. Phys. Lett.. 2008;93(3) 033307-033303
- [Google Scholar]
- Humidity sensors using in situ synthesized sodium polystyrenesulfonate/ZnO nanocomposites. Talanta. 2004;62(4):707-712.
- [Google Scholar]
- Arylamine organic dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Soc. Rev.. 2013;42(8):3453-3488.
- [Google Scholar]
- Hybrid solar cells from P3HT and silicon nanocrystals. Nano Lett.. 2008;9(1):449-452.
- [Google Scholar]
- The relationship between intermolecular interactions and charge transport properties of trifluoromethylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Org. Electron.. 2014;15(9):1896-1905.
- [Google Scholar]
- Makoto Satsuki, N.I., Sadaharu Suga, Hisayoshi Fujikawa, Yasunori Taga, 2007. Organic light emitters using coumarin derivative as luminescent agents having efficiency and durability; display panels. US7252892 B2.
- Electron transfer reactions in chemistry. Theory and experiment. Rev. Mod. Phys.. 1993;65(3):599-610.
- [Google Scholar]
- Materials science: semiconductors grown large and thin. Nature. 2015;520(7549):631-632.
- [Google Scholar]
- Dye-sensitized solar cells with 13% efficiency achieved through the molecular engineering of porphyrin sensitizers. Nat. Chem.. 2014;6(3):242-247.
- [Google Scholar]
- Calculation of the photocurrent-potential characteristic for regenerative, sensitized semiconductor electrodes. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 1996;44(2):119-155.
- [Google Scholar]
- Nalwa, H.S., 2001. Handbook of Advanced Electronic and Photonic Materials and Devices. Academic, San Diego CA.
- Fluorescence water sensor based on covalent immobilization of chalcone derivative. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2006;577(2):264-270.
- [Google Scholar]
- A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature. 1991;353(6346):737-740.
- [Google Scholar]
- Ab initio determination of ground and excited state oxidation potentials of organic chromophores for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2010;114(51):22742-22750.
- [Google Scholar]
- A computational investigation of organic dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells: benchmark, strategies, and open issues. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2010;114(15):7205-7212.
- [Google Scholar]
- Quantum chemical calculations of the influence of anchor-cum-spacer groups on femtosecond electron transfer times in dye-sensitized semiconductor nanocrystals. J. Chem. Theory Comput.. 2006;2(2):441-451.
- [Google Scholar]
- Photoinduced electron-transfer processes along molecular wires based on phenylenevinylene oligomers: a quantum-chemical insight. J. Am. Chem. Soc.. 2002;124(16):4436-4447.
- [Google Scholar]
- Photoinduced energy-transfer and electron-transfer processes in dye-sensitized solar cells: TDDFT insights for triphenylamine dyes. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2010;114(39):16716-16725.
- [Google Scholar]
- Design of new triphenylamine-sensitized solar cells: a theoretical approach. Environ. Sci. Technol.. 2010;44(14):5666-5671.
- [Google Scholar]
- Enhanced efficiency of organic dye-sensitized solar cells: triphenylamine derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2009;113(38):16821-16833.
- [Google Scholar]
- Optimizing dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.. 2006;45(15):2338-2345.
- [Google Scholar]
- Design rules for donors in bulk-heterojunction solar cells—towards 10% energy-conversion efficiency. Adv. Mater.. 2006;18(6):789-794.
- [Google Scholar]
- Real-time propagation of the reduced one-electron density matrix in atom-centered Gaussian orbitals: application to absorption spectra of silicon clusters. J. Chem. Phys.. 2007;127(23) 234107-234107
- [Google Scholar]
- Gas and humidity sensors based on iron oxide–polypyrrole nanocomposites. Sens. Actuators B: Chem.. 2002;81(2):277-282.
- [Google Scholar]
- Low-cost dyes based on methylthiophene for high-performance dye-sensitized solar cells. Dyes Pigm.. 2010;87(3):181-187.
- [Google Scholar]
- Ceramic thin films by sol-gel processing as novel materials for integrated humidity sensors. Sens. Actuators B: Chem.. 1996;31(1):59-70.
- [Google Scholar]
- Organic—inorganic hybrid solar cells: a comparative review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2012;107:87-111.
- [Google Scholar]
- New triphenylamine-based dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2008;112(3):874-880.
- [Google Scholar]
- Origin of the open-circuit voltage of organic thin-film solar cells based on conjugated polymers. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2009;93(6–7):759-761.
- [Google Scholar]
- Theoretical studies on the geometrical and electronic structures of N-methyle-3,4-fulleropyrrolidine. J. Mol. Struct. (Thoechem). 2008;862(1–3):98-104.
- [Google Scholar]
- Employ a bisthienothiophene linker to construct an organic chromophore for efficient and stable dye-sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci.. 2009;2(1):92-95.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cyano or o-nitrophenyl? Which is the optimal electron-withdrawing group for the acrylic acid acceptor of D-π-A sensitizers in DSSCs? A density functional evaluation. J. Mol. Model.. 2013;19(4):1597-1604.
- [Google Scholar]
- Density functional theory characterization and design of high-performance diarylamine-fluorene dyes with different [small pi] spacers for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem.. 2012;22(2):568-576.
- [Google Scholar]
- Synthesis, photophysical and electrochemical properties of two novel carbazole-based dye molecules. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc.. 2015;135:379-385.
- [Google Scholar]







