Translate this page into:
Analysis of Newtonian heating and higher-order chemical reaction on a Maxwell nanofluid in a rotating frame with gyrotactic microorganisms and variable heat source/sink
⁎Corresponding author. mramzan@bahria.edu.pk (Muhammad Ramzan)
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
This article was originally published by Elsevier and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Peer review under responsibility of King Saud University.
Abstract
The goal of this study is to investigate the rotating Maxwell nanoliquid flow incorporating gyrotactic microbes with Newtonian heating and irregular heat source sink. The motion of the flow is induced due to linearly unidirectional elongated surface. The uniqueness of the flow is enhanced by the inclusion of additional phenomenon of higher order chemical reaction incorporated with Darcy Forchheimer flow, Fourier and Fick law. Numerical solution of the formulated problem is developed via bvp4c function in MATLAB. The influence of the embroiled parameters on the flow distribution is demonstrated through various graphs and tables. It is noticed that fluid velocity declines on incrementing the rotation parameter. An upsurge in thermal field is portrayed on augmenting the Newtonian heating. Comparative analysis of the results of the proposed model with previous published research is included which confirms the validity of the current model.
Keywords
Maxwell nanofluid
Newtonian heating
Rotating flow
Gyrotactic microorganisms
Higher order chemical reaction
Symbol
Description
Symbol
Description
Conjugate parameter for heat transfer
Relaxation time parameter for concentration
Chemotaxis constant
Chemical reaction
Magnetic field strength
Bioconvection Lewis number
Fluid concentration
Brownian motion parameter
Wall concentration
Thermophoresis parameter
Ambient concentration
Local Nusselt number
Drag coefficient
Local motile density number
Specific heat
Bioconvection Peclet number
Skin friction coefficient
Prandtl number
Space dependent source/sink parameter
Heat flux
Brownian diffusion coefficient
Mass flux
Diffusivity of microorganisms
Motile flux
Thermophoretic diffusion coefficient
Motile microorganisms
Non-dimensional fluid relaxation time
Local Reynold number
Non-uniform inertia coefficient of porosity
Schmidt number
Forchheimer number
Local Sherwood number
temperature dependent source/sink parameter
Order of reaction
Magnetic parameter
Fluid temperature
Heat transfer coefficient
ambient temperature
Thermal conductivity
velocity component
Relaxation time parameter for temperature
Maximum speed of swimming cell
Symbol
Description
Symbol
Description
Kinematic viscosity
Dimensionless Chemical reaction rate
Dynamic viscosity
Fluid moderation time
Angular velocity
Electrical conductivity
density
Bioconvection concentration difference parameter
Rotation parameter
Ratio between heat capacities
Porosity number
1 Introduction
Boundary layer flow over a deforming surface is immensely acknowledged by the scholars owing to its vast applications such as the, metallurgical process, glass blowing, production of rubber and plastic sheets aerodynamics, and extrusion, etc. Fluid flow on a deforming sheet was instigated by Crane (1970). Sreedevi and Reddy (2020) illustrated the behavior of chemical reaction with thermal radiation on a three-dimensional 3D Maxwell nanofluid past a deforming surface. It is observed in this investigation that by increasing the Deborah number the fluid velocity diminishes. On a Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) Maxwell graphene nanofluid flow, the outcome of thermal radiation past a horizontal deforming surface is scrutinized by Hussain et al. (2020) in the presence of thermal slip condition. Ali et al. (2019) numerically examined Maxwell nano liquid flow on an exponential deforming surface. The impact of chemical reaction incorporated with thermal radiation is investigated by Prabhavathi et al. (2018) on a Maxwell nano liquid flow. On Maxwell nanoliquid flow Kundu et al. (2018) analyzed Cattaneo Christov (CC) model with slip effects past a nonlinear elongated surface (Table 1).
Authors
3D flow
Variable heat source/sink
Darcy Forchheimer flow
Gyrotactic microorganisms
Rotating frame
Newtonian heating
Hayat et al. (2019)
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Shafiq et al. (2020)
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Sohail et al. (2020)
Yes
No
No
Yes
No
No
Ramzan (2015)
Yes
No
No
No
No
Yes
Present
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Non-Newtonian fluid flow on a stretching surface in a rotating frame has enormously been emphasized by the researchers due to its vast applications in geophysical processes and engineering and such as food treatments, disk cleaners, rotor systems, and gas turbines. Aziz et al. (2019) analytically investigated the behavior of homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions and Darcy Forchheimer on a 3D nanofluid in a rotating flow on a stretchable sheet. Shah et al. (2019) presented an analytical solution for 3D nanofluid with Cattaneo-Christov (CC) model in a rotating frame past a linearly elongated surface. It is found that by amplifying the nanoparticle fraction the fluid velocity upsurges, whereas, temperature field decays. Alzahrani et al. (2019) has discussed the impact of Darcy Forchheimer with heat generation/absorption on micropolar nano liquid between two parallel rotating plates. They found twofold flow behavior in the fluid velocity by escalating the inertia coefficient and rotating parameter. Recent studies on a Darcy Forchheimer nano liquid in a rotating outline can be seen in (Ullah et al., 2020; Hayat et al., 2019; Shafiq et al., 2020; Ramaiah et al., 2020; Hayat et al., 2020).
Non-uniform heat source and sink has broad range of applications which includes unrefined oil extraction, cooling of metal sheets and radial diffusers. The impact of irregular heat source/sink, Joule dissipation is explored by Thumma and Mishra (2020) on a 3D Eyring-Powell nanofluid on a deformable surface. Jakati et al. (2019) illustrated the effect of irregular heat on a 2D Maxwell nanofluid on a linear stretchable surface. On a micropolar fluid flow second order velocity slip amalgamated with irregular heat source sink is investigated by Kumar et al. (2019) past an elongated sheet. Khan et al. (2018) studied the impact of Darcy Forchheimer on a micropolar nanofluid in a rotating flow between two parallel plates.
A minuscule organism is considered as microscopic organisms (microorganisms) as it can be perceived via an optical microscope. They are found everywhere like in water, air, soil, rocks, plants, animals, and even in the human body. Cholera, meningitis, anthrax, citrus canker, and tuberculosis are a few diseases caused by microorganisms. Gyrotactic microorganisms are those organisms that move in stagnant water against gravity and depend on the type of species. Due to the random movement of microorganisms, the phenomenon of bio-convection arises. This micro-organisms characteristic is used in biotechnology, sedimentary basin, bioreactors, biosensors, separation of non-living and living cells. Abbasi et al. (2020) numerically analyzed Brownian motion, thermophoresis effect, and impact of bio-convection on Maxwell nanofluid past a linear deforming sheet. The effect of gyrotactic microorganisms with thermal radiation is analytically addressed by Ahmad et al. (2020) on a three-dimensional (3D) Maxwell nanofluid on an oscillatory deforming surface. Khan and Nadeem (2020) exhibited the aftermath of the magnetic field with viscous dissipation and chemical reaction on Maxwell nano liquid past an exponentially extending surface with variable slip conditions. Sohail et al. (2020) focused on gyrotactic microorganisms with homogeneous – heterogeneous reactions on a Maxwell nano liquid over a stretchable sheet incorporated with heat generation/absorption effects.
Transmission of heat and mass incorporated with chemical reaction has widespread applications such as food processing, destruction of harvests due to freezing, paper manufacturing and ceramics. Narender et al. (2020) numerically illustrated viscous dissipation on an incompressible 2D nanofluid flow on a linear elongated surface with chemical reaction. Ibrahim and Negera (2020) numerically inspected the impact of stagnation point flow on a Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) upper convected Maxwell fluid with chemical reaction along a deforming surface. On an unsteady chemically reactive viscous flow Ijaz et al. (2020) addressed Joule heating and activation energy in a rotating frame on a stretchable sheet. On a chemically reactive Maxwell nanoliquid flow Khan et al. (2019) numerically examined the behavior of Cattaneo-Christov model over a deformable sheet.
Great amount of research is done on a rotating flow past a linear extending surface. The study of MHD Maxwell nanofluid influenced by gyrotactic microorganisms and higher-order chemical reaction in a rotating flow is still scarce and yet not discussed in the literature. The uniqueness of the problem is exacerbated by the combined effect of Newtonian heating and variable heat source/sink. MATLAB built-in function bvp4c is used to solve the specified mathematical problem. The influence of the pertinent parameters on the present analysis is illustrated graphically. The following questions are the aim of the research.
-
What is the influence of augmenting the fluid relaxation and rotation parameter on the fluid velocity?
-
What effect does the conjugate parameter have on the thermal field?
-
What is the aftermath of order of chemical reaction on the fluid concentration?
-
Impact of Peclet number on the motile density profile?
2 Problem formulation
3D Darcy Forchheimer rotating flow of MHD Maxwell nanoliquid is examined on a stretchable linear surface with Newtonian heating. The sheet deforms in the
The surface is associated in the
and the fluid is considered at
(Fig. 1). The fluid spins about the
with constant angular velocity
. The effect of higher order chemical reaction, gyrotactic microbes incorporated with variable heat source and sink are additional phenomenon to enhance the uniqueness of the flow. The characteristics of Fourier and Fick law are inspected.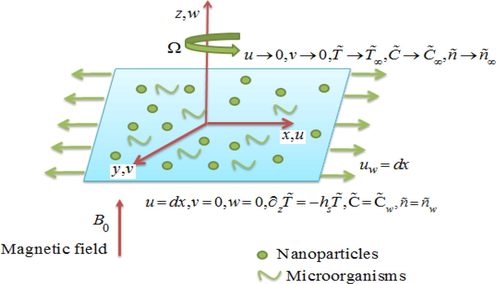
Flow configuration of the model.
The innovative model is regulated by the following system of equations (Shafiq et al., 2020; Ramaiah et al., 2020):
Using appropriate transformation (Aziz et al., 2019; Sohail et al., 2020; Ramzan and Yousaf, 2015):
By utilizing the above transformation equation (1) is trivially equated. However, equations
(2) - (6) and (8) take the form:
and
The mathematical forms of surface drag force, temperature gradient are specified as:
By utilizing equation (9), equation (16) - (18) are transmuted as:
3 Numerical solution
Numerous analytical, exact and numerical techniques (Xia et al., 2021; Wakif et al., 2021; Rasool and Wakif, 2021; Wakif et al., 2021; Wakif et al., 2020; Alghamdi et al., 2021; Thumma et al., 2020; Shaheen et al., 2021; Wakif and Sehaqui, 2020; Chen et al., 2021) can be used to solve the system of ODEs. The exact solution of highly nonlinear coupled system of ODEs (10)-(14), with the boundary conditions (15) is not possible. Numerical solution of the flow model is computed via bvp4c function in MATLAB. The numerical procedure is given below:
4 Graphical analysis
The main focus of this section is to explore the impact of various physical factors on involved profiles. For the graphical analysis of the non-dimensional parameters following numerical values are taken
.
Figs. 2 & 3 depicts the behavior of
velocity
and
of velocity
. The behavior of numerous values of non-dimensional fluid relaxation time
on
and
is illustrated in Figs. 2(a) and 2(b). Fig. 2(a) percepts that as
has direct proportionate to fluid moderation time
. By augmenting
, fluid moderation time boosts which halts the fluid flow. Eventually, it is perceived that
drops. Fig. 2(b) shows that on incrementing the fluid relaxation time
increases adjacent to the wall, while it decreases in magnitude away from the wall. Negative values of
exhibits that flow due to rotational effect is only in the direction of
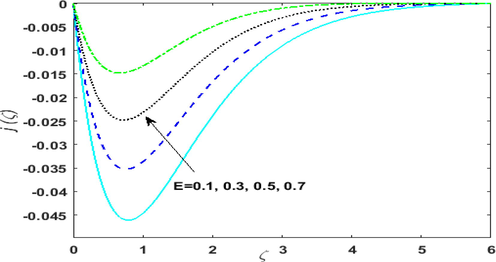
The impact of rotation parameter
on the velocity field is deliberated in Figs. 3(a) and 3(b). Since
, so by augmenting
angular velocity increases. The fluid is rotating and flowing. By enlarging
the rotation rate increases in contrast to the stretching rate. Therefore,
decreases as the motion of the fluid slow down. Fig. 3(a) shows that
is dwindling function of
. Fig. 3(b) exhibits an oscillatory configuration for escalating values of
. The rotation parameter plays a major role in accelerating the flow in
direction. It is seen that
descends and the fluid accelerates in the y-direction.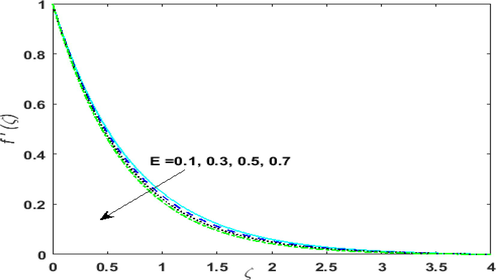
Impact of fluid relaxation time on
Impact of fluid relaxation time on
Behavior of rotation parameter on
Behavior of rotation parameter on
The impression of conjugate parameter
on thermal field
is portrayed in Fig. 4. The rate of heat transmission is accelerated on augmenting
. This is due to the transfer of heat from the heated surface to the cold fluid. This elevates
. The outcome of variable source and sink parameter on
is sketched in Figs. 5(a)-5(d). Growing values of
corresponds to irregular heat source implying that more heat is generated. Thus, an upsurge is noticed in
. Influence of irregular heat sink i.e
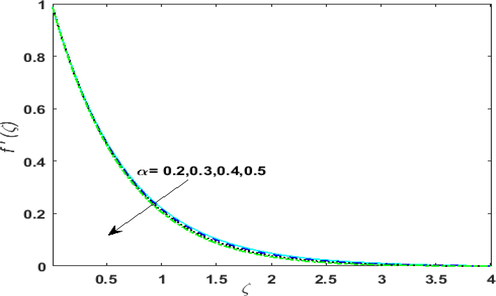
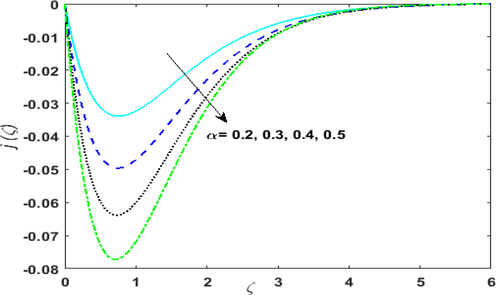
is shown in Figs. 5(c) & 5 (d) corresponds to absorption of heat. Therefore, thermal field deteriorates. Fig. 6 portrays the effect of growing values of higher-order reaction
on
. By upsurging
, the rate of mass transfer is enhanced. Hence,
rises. Variation of Peclet number on motile density profile is portrayed in Fig. 7. On incrementing Peclet number diffusion of microorganisms decreases. Hence, motile density of fluid diminishes. The impact of
on local Nusselt number is described in Table 2. It is noticed that by increasing
the rate of heat transfer enhances. However,
decays for larger values of E. Table 3 shows an outstanding correlation of the current outcome for the rotation parameter with Nazar et al. (2004), Wang (1988), and Ali et al. (2020).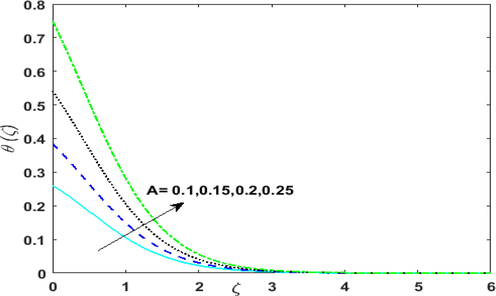
Behavior of conjugate heat parameter on
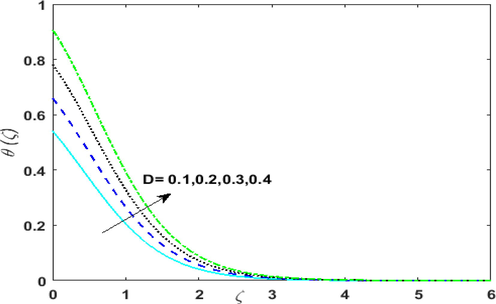
Impact of variable space dependent source parameter
on
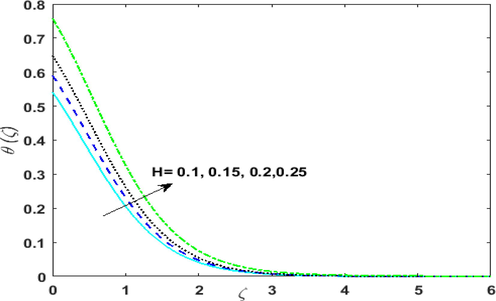
Impact of variable temperature dependent source parameter
on
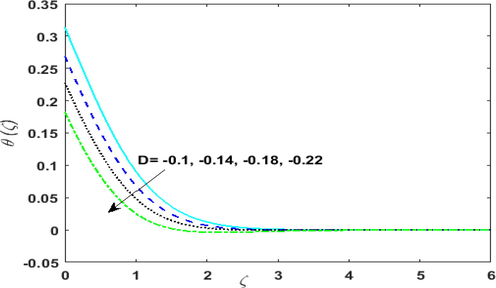
Impact of variable space dependent sink parameter
on
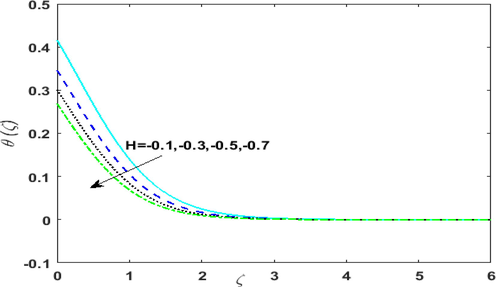
Impact of variable temperature dependent sink parameter
on
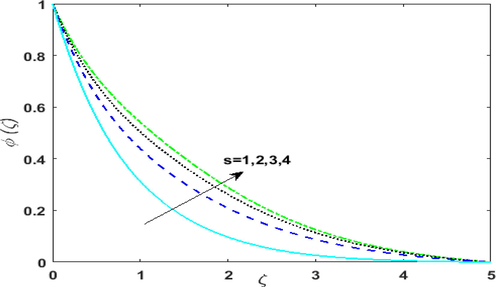
Outcome of higher order reaction on
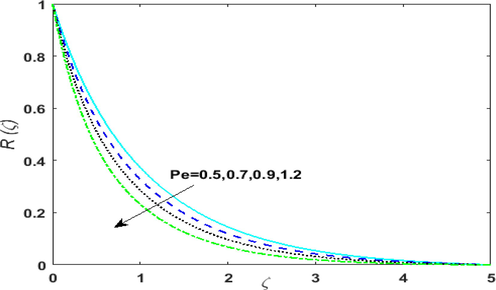
Outcome of Peclet number on
0.1
0.1241273
0.2
0.2962659
0.3
0.5595729
0.6
0.1297434
0.7
0.12980309
0.8
0.12986562
0.5
0.13087804
0.6
0.1295171
0.7
0.1264253
Nazar (2004)
Wang (1988)
Ali (2020)
Present
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
0.5
1.1384
0.5128
1.1384
0.5128
1.13844
0.51283
1.13848
0.51268
1
1.3250
0.8371
1.3250
0.8371
1.32501
0.83715
1.32501
0.83712
2
1.6523
1.2873
1.6523
1.2873
1.65232
1.28732
1.65235
1.28726
5
–
–
–
–
2.39026
2.15024
2.39014
2.15053
5 Concluding remarks
Numerical solution for MHD Maxwell nanofluid with gyrotactic microorganisms, a higher-order chemical reaction in the presence of variable source/sink, and Newtonian heating is investigated in a rotating flow on a deformable surface. The flow is analyzed with additional effect of Darcy Forchheimer flow amalgamated with modified Fourier and Fick laws. Numerical solution of the flow model is computed via bvp4c function in MATLAB. The following are the notable outcomes of the current investigation:
-
Fluid velocity deteriorates on incrementing the rotation parameter.
-
On escalating fluid relaxation time declines, whereas, for opposite outcome is observed.
-
By augmenting the conjugate heat parameter amplifies.
-
For larger values of higher order chemical reaction solutal field escalates.
-
For higher estimation of Peclet number, the motile density deteriorates.
-
On incrementing the conjugate heat parameter and thermal relaxation time rate of heat transfer augments.
-
The rate of heat transfer decreases on varying the fluid relaxation time.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest regarding this publication.
7 Author contribution statement
M.R. supervised and conceived the idea; N.S wrote the manuscript; J.D.C. & S.K. did the software work; Y.M.C. did funding arrangements; F.W. helped in graphical depiction; M.Y.M. and H.A.S.G. helped in revising the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University, Abha 61413, Saudi Arabia for funding this work through research groups program under Grant Number R.G.P-1/88/42.
References
- Flow past a stretching plate. Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik ZAMP. 1970;21(4):645-647.
- [Google Scholar]
- Combined influence of Brownian motion and thermophoresis on Maxwell three-dimensional nanofluid flow over stretching sheet with chemical reaction and thermal radiation. J. Porous Media. 2020;23(4):327-340.
- [Google Scholar]
- Hydromagnetic dissipative and radiative graphene Maxwell nanofluid flow past a stretched sheet-numerical and statistical analysis. Mathematics. 2020;8(11):1929.
- [Google Scholar]
- Heat and mass transfer analysis of 3D Maxwell nanofluid over an exponentially stretching surface. Phys. Scr.. 2019;94(6):065206.
- [Google Scholar]
- Heat and mass transfer enhancement of SWCNTs and MWCNTs based Maxwell nanofluid flow over a vertical cone with slip effects. Powder Technol.. 2018;340:253-263.
- [Google Scholar]
- Framing the Cattaneo-Christov heat flux phenomena on CNT-based Maxwell Nanofluid along stretching sheet with multiple slips. Arab. J. Sci. Eng.. 2018;43(3):1177-1188.
- [Google Scholar]
- Influence of homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions in the three-dimensional rotating flow of a nanofluid subject to Darcy-Forchheimer porous medium: an optimal analysis. Phys. Scr.. 2019;94(11):115708.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo-Christov heat flux model for three-dimensional rotating flow of SWCNT and MWCNT nanofluid with Darcy-Forchheimer porous medium induced by a linearly stretchable surface. Symmetry. 2019;11(3):331.
- [Google Scholar]
- Darcy-forchheimer radiative flow of micropoler CNT nanofluid in rotating frame with convective heat generation/consumption. Processes. 2019;7(10):666.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Significance of Arrhenius activation energy in Darcy-Forchheimer 3D rotating flow of nanofluid with radiative heat transfer. Physica A. 2020;550:124024
- [Google Scholar]
- Numerical simulation for Darcy-Forchheimer three-dimensional rotating flow of nanofluid with prescribed heat and mass flux conditions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim.. 2019;136(5):2087-2095.
- [Google Scholar]
- Significance of thermal slip and convective boundary conditions in three dimensional rotating Darcy-Forchheimer nanofluid flow. Symmetry. 2020;12(5):741.
- [Google Scholar]
- MHD rotating flow of a Maxwell fluid with Arrhenius activation energy and non-Fourier heat flux model. Heat Transfer. 2020;49(4):2209-2227.
- [Google Scholar]
- Significance of homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions in Darcy-Forchheimer three-dimensional rotating flow of carbon nanotubes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim.. 2020;139(1):183-195.
- [Google Scholar]
- Effect of nonuniform heat source/sink, and viscous and Joule dissipation on 3D Eyring-Powell nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet. J. Comput. Design Eng. 2020
- [Google Scholar]
- Study of Maxwell Nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet with non-uniform heat source/sink with external magnetic field. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Thermal Sci.. 2019;55:218-232.
- [Google Scholar]
- Simultaneous solutions for first order and second order slips on micropolar fluid flow across a convective surface in the presence of Lorentz force and variable heat source/sink. Sci. Rep.. 2019;9(1):1-14.
- [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A., Shah, Z., Islam, S., Khan, S., Khan, W., Khan, A. Z. (2018). Darcy–Forchheimer flow of micropolar nanofluid between two plates in the rotating frame with non-uniform heat generation/absorption. Adv. Mech. Eng., 10(10), 1687814018808850.
- Stagnation point flow of Maxwell nanofluid containing gyrotactic micro-organism impinging obliquely on a convective surface. Heat Transfer. 2020;49(5):2977-2999.
- [Google Scholar]
- Thermally developed Cattaneo-Christov Maxwell nanofluid over bidirectional periodically accelerated surface with gyrotactic microorganisms and activation energy. Alexandria Eng. J.. 2020;59(6):4865-4878.
- [Google Scholar]
- Theoretical treatment of bio-convective Maxwell nanofluid over an exponentially stretching sheet. Can. J. Phys.. 2020;98(8):732-741.
- [Google Scholar]
- On the onset of entropy generation for a nanofluid with thermal radiation and gyrotactic microorganisms through 3D flows. Phys. Scr.. 2020;95(4):045206.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Narender, G., Govardhan, K., Sarma, G. S. (2020). Convection of Maxwell nanofluid with the effects of viscous dissipation and chemical reaction over a stretching sheet. In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 2246, No. 1, p. 020052). AIP Publishing LLC.
- MHD slip flow of upper-convected Maxwell nanofluid over a stretching sheet with chemical reaction. J. Egypt. Math. Soc.. 2020;28(1):7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Binary chemical reaction with activation energy in rotating flow subject to nonlinear heat flux and heat source/sink. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2020
- [Google Scholar]
- Generalized diffusion effects on Maxwell nanofluid stagnation point flow over a stretchable sheet with slip conditions and chemical reaction. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng.. 2019;41(3):138.
- [Google Scholar]
- Boundary layer flow of three-dimensional viscoelastic nanofluid past a bi-directional stretching sheet with Newtonian heating. AIP Adv.. 2015;5(5):057132.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Gear-generalized differential quadrature analysis of oscillatory convective Taylor-Couette flows of second-grade fluids subject to Lorentz and Darcy-Forchheimer quadratic drag forces. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer. 2021;126:105395.
- [Google Scholar]
- Wakif, A., Animasaun, I. L., Sehaqui, R. (2021). A Brief Technical Note on the Onset of Convection in a Horizontal Nanofluid Layer of Finite Depth via Wakif-Galerkin Weighted Residuals Technique (WGWRT). In Defect and Diffusion Forum (Vol. 409, pp. 90-94). Trans Tech Publications Ltd.
- Numerical spectral examination of EMHD mixed convective flow of second-grade nanofluid towards a vertical Riga plate using an advanced version of the revised Buongiorno’s nanofluid model. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim.. 2021;143(3):2379-2393.
- [Google Scholar]
- Thermal radiation and surface roughness effects on the thermo-magneto-hydrodynamic stability of alumina–copper oxide hybrid nanofluids utilizing the generalized Buongiorno's nanofluid model. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim.. 2021;143(2):1201-1220.
- [Google Scholar]
- Novel physical insights into the thermodynamic irreversibilities within dissipative EMHD fluid flows past over a moving horizontal riga plate in the coexistence of wall suction and joule heating effects: a comprehensive numerical investigation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng.. 2020;45(11):9423-9438.
- [Google Scholar]
- Significance of variability in magnetic field strength and heat source on the radiative-convective motion of sodium alginate-based nanofluid within a Darcy-Brinkman porous structure bounded vertically by an irregular slender surface. Case Studies. Therm. Eng.. 2021;28:101428.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Thumma, T., Wakif, A., Animasaun, I. L. (2020). Generalized differential quadrature analysis of unsteady three‐dimensional MHD radiating dissipative Casson fluid conveying tiny particles. Heat Transfer, 49(5), 2595-2626.
- Soret-Dufour impact on a three-dimensional Casson nanofluid flow with dust particles and variable characteristics in a permeable media. Sci. Rep.. 2021;11(1):1-21.
- [Google Scholar]
- Wakif, A., Sehaqui, R. (2020). Generalized differential quadrature scrutinization of an advanced MHD stability problem concerned water‐based nanofluids with metal/metal oxide nanomaterials: a proper application of the revised two‐phase nanofluid model with convective heating and through‐flow boundary conditions. Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations.
- Thermophoretic particle deposition in the flow of dual stratified Casson fluid with magnetic dipole and generalized Fourier's and Fick's laws. Case Studies Thermal Eng.. 2021;26:101186
- [Google Scholar]
- Unsteady boundary layer flow due to a stretching surface in a rotating fluid. Mech. Res. Commun.. 2004;31(1):121-128.
- [Google Scholar]
- Stretching a surface in a rotating fluid. Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik ZAMP. 1988;39(2):177-185.
- [Google Scholar]
- Unsteady magneto-hydrodynamic transport of rotating Maxwell nanofluid flow on a stretching sheet with Cattaneo-Christov double diffusion and activation energy. Thermal Sci. Eng. Prog.. 2020;20:100720
- [Google Scholar]







